MLflow 3
Discover the next generation of MLflow, designed to streamline your AI experimentation and accelerate your journey from idea to production. MLflow 3 brings cutting-edge support for GenAI workflows, enabling seamless integration of generative AI models into your projects.
What is MLflow 3?
MLflow 3 delivers best-in-class experiment tracking, observability, and performance evaluation for machine learning models, AI applications, and agents! With MLflow 3, it's now easier than ever to:
- Centrally track and analyze the performance of your models, prompts, agents, and AI applications across all environments, from interactive queries in a development notebook through production batch or real-time serving deployments.
- Select the best models, prompts, agents, and AI applications for production with an enhanced performance comparison experience powered by MLflow's tracing and evaluation capabilities.
What's New in MLflow 3?
Here are the short highlights of what's new in MLflow 3:
MLflow 3 introduces versioning mechanism purpose-built for GenAI applications not only model artifacts. The new LoggedModel entity serves as a metadata hub, linking each conceptual application version to its specific external code (e.g., a Git commit), configurations, with other MLflow entities like traces and evaluation runs. The new versioning mechanism also work seamlessly for traditional ML models and deep learning checkpoints.
Enhanced model tracking provides comprehensive lineage between models, runs, traces, prompts, and evaluation metrics. The new model-centric design allows you to group traces and metrics from different development environments and production, enabling rich comparisons across model versions.
MLflow's evaluation and monitoring capabilities help you systematically measure, improve, and maintain the quality of your GenAI applications throughout their lifecycle. From development through production, use the same quality scorers to ensure your applications deliver accurate, reliable responses while managing cost and latency.
Real-world GenAI applications need human oversight. MLflow 3 now tracks human annotations and feedback for model predictions, enabling streamlined human-in-the-loop evaluation cycles. This creates a collaborative environment where data scientists, domain experts, and stakeholders can efficiently improve model quality together. (Note: Currently available in Databricks Managed MLflow. Open source release coming in the next few months.)
Transform prompt engineering from art to science. The MLflow Prompt Registry now includes prompt optimization capabilities built on top of the state-of-the-art research, allowing you to automatically improve prompts using evaluation feedback and labeled datasets. This includes versioning, tracking, and systematic prompt engineering workflows.
The MLflow documentation and website has been fully redesigned to support two main user journeys: GenAI development and classic machine learning workflows. The new structure offers dedicated sections for GenAI features (including LLMs, prompt engineering, and tracing), and traditional ML capabilities such as experiment tracking, model registry, deployment, and evaluation.
Getting Started
Install MLflow 3 by running the following command:
pip install 'mlflow>=3.1'
Resources: 🌐 New Website | 📖 Documentation | 🎉 Release Notes
Quickstart
Prerequisites
Run the following command to install MLflow 3 and OpenAI packages.
pip install mlflow openai -U
Set OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable in CLI to authenticate to OpenAI APIs.
export OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
This quickstart demonstrates how to create a generative AI application with prompt engineering and evaluate it using MLflow 3. It highlights the integration of the LoggedModel lineage feature with runs and traces, showcasing seamless tracking and observability for GenAI workflows.
Register a prompt template
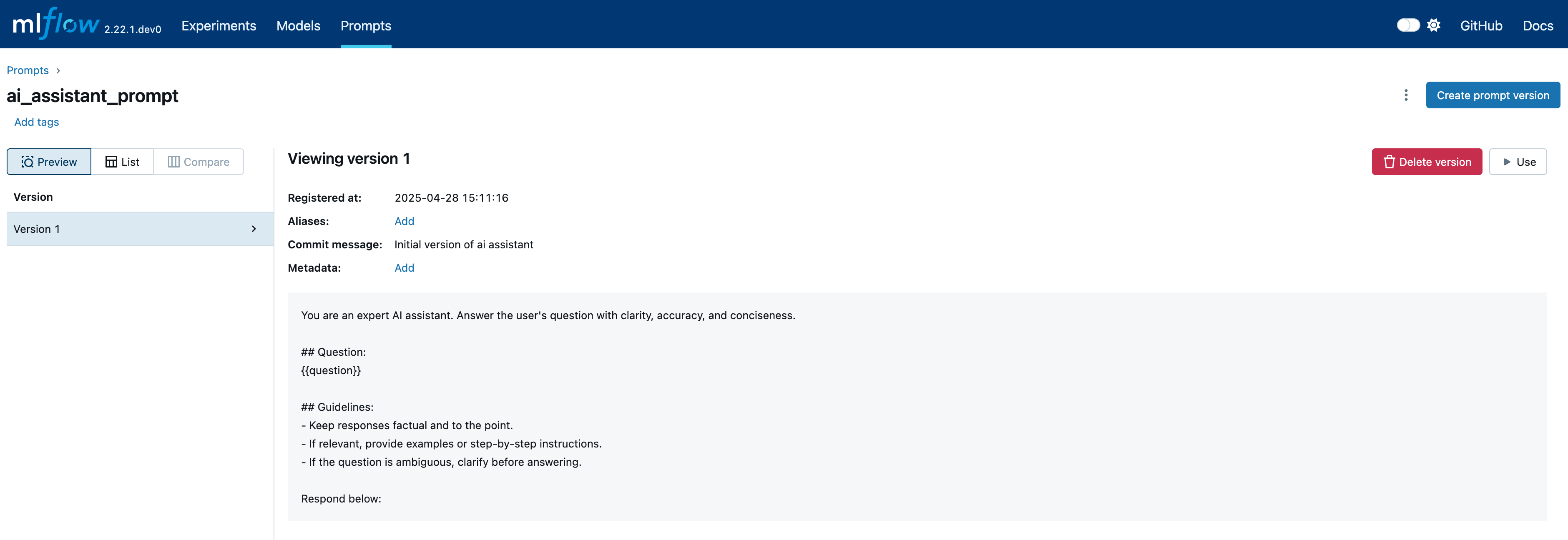
First, we create a prompt template and register it with MLflow Prompt Registry.
import mlflow
# define a prompt template
prompt_template = """\
You are an expert AI assistant. Answer the user's question with clarity, accuracy, and conciseness.
## Question:
{{question}}
## Guidelines:
- Keep responses factual and to the point.
- If relevant, provide examples or step-by-step instructions.
- If the question is ambiguous, clarify before answering.
Respond below:
"""
# register the prompt
prompt = mlflow.genai.register_prompt(
name="ai_assistant_prompt",
template=prompt_template,
commit_message="Initial version of AI assistant",
)
Switch to the Prompts tab to view the registered prompt:
Make a request to OpenAI
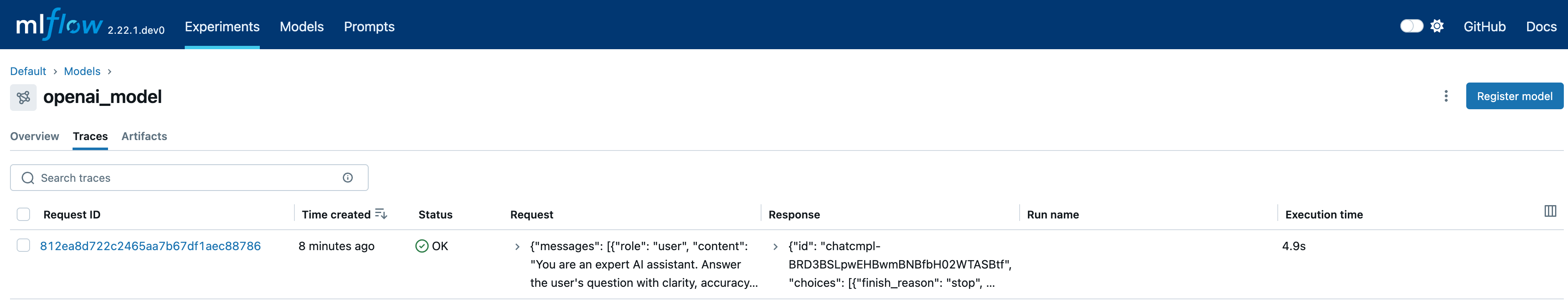
At this step, we set an active model for grouping traces. After enabling autologging, all traces generated during requests will be linked to the active model.
from openai import OpenAI
# set an active model for linking traces, a model named `openai_model` will be created
mlflow.set_active_model(name="openai_model")
# turn on autologging for automatic tracing
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Initialize OpenAI client
client = OpenAI()
question = "What is MLflow?"
response = (
client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt.format(question=question)}],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=2000,
)
.choices[0]
.message.content
)
# get the active model id
active_model_id = mlflow.get_active_model_id()
print(f"Current active model id: {active_model_id}")
mlflow.search_traces(model_id=active_model_id)
# trace_id trace ... assessments request_id
# 0 7bb4569d3d884e3e87b1d8752276a13c Trace(trace_id=7bb4569d3d884e3e87b1d8752276a13c) ... [] 7bb4569d3d884e3e87b1d8752276a13c
# [1 rows x 12 columns]
Generated traces can be viewed in the Traces tab of the logged model:
Evaluate the response with GenAI metrics
Finally, we evaluate the response using different metrics and record the results to a run and the current active model.
from mlflow.metrics.genai import answer_correctness, answer_similarity, faithfulness
# ground truth result for evaluation
mlflow_ground_truth = (
"MLflow is an open-source platform for managing "
"the end-to-end machine learning (ML) lifecycle. It was developed by Databricks, "
"a company that specializes in big data and machine learning solutions. MLflow is "
"designed to address the challenges that data scientists and machine learning "
"engineers face when developing, training, and deploying machine learning models."
)
# Define evaluation metrics
metrics = {
"answer_similarity": answer_similarity(model="openai:/gpt-4o"),
"answer_correctness": answer_correctness(model="openai:/gpt-4o"),
"faithfulness": faithfulness(model="openai:/gpt-4o"),
}
# Calculate metrics based on the input, response and ground truth
# The evaluation metrics are callables that can be invoked directly
answer_similarity_score = metrics["answer_similarity"](
predictions=response, inputs=question, targets=mlflow_ground_truth
).scores[0]
answer_correctness_score = metrics["answer_correctness"](
predictions=response, inputs=question, targets=mlflow_ground_truth
).scores[0]
faithfulness_score = metrics["faithfulness"](
predictions=response, inputs=question, context=mlflow_ground_truth
).scores[0]
# Start a run to represent the evaluation process
with mlflow.start_run() as run:
# Log metrics and pass model_id to link the metrics
mlflow.log_metrics(
{
"answer_similarity": answer_similarity_score,
"answer_correctness": answer_correctness_score,
"faithfulness": faithfulness_score,
},
model_id=active_model_id,
)
Navigate to the Models tab of the experiment to view the newly created LoggedModel. Evaluation metrics, model ID, source run, parameters, and other details are displayed on the models detail page, providing a comprehensive overview of the model's performance and lineage.
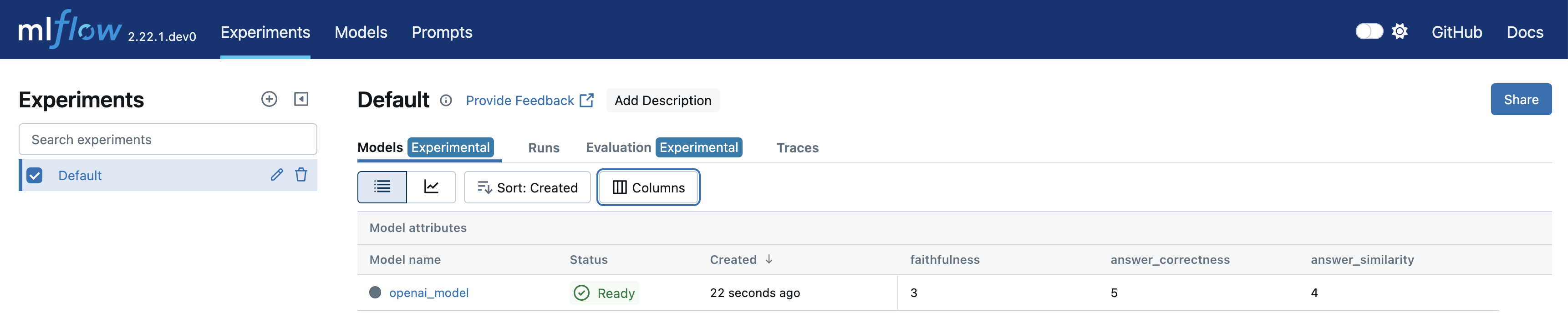
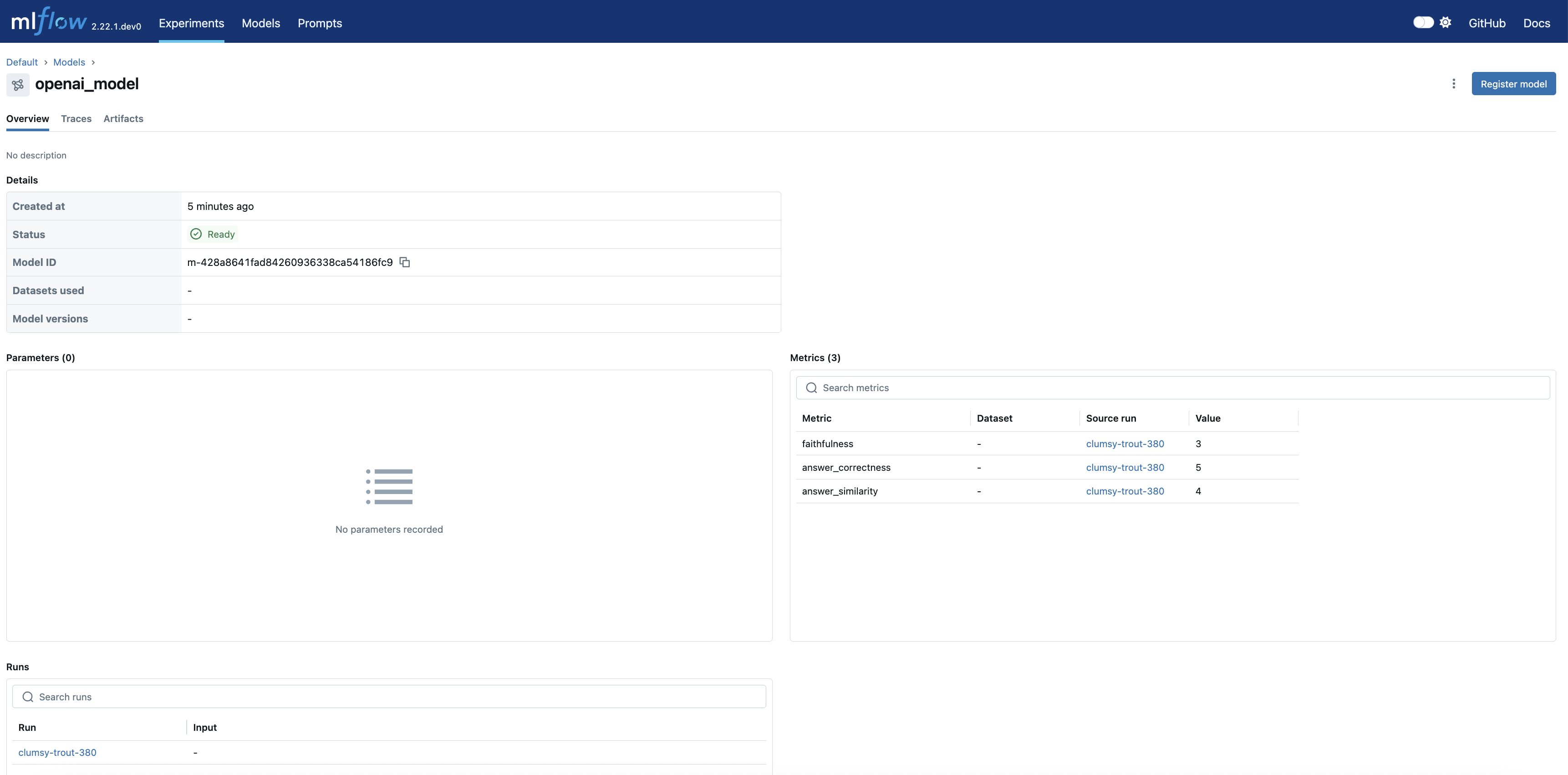
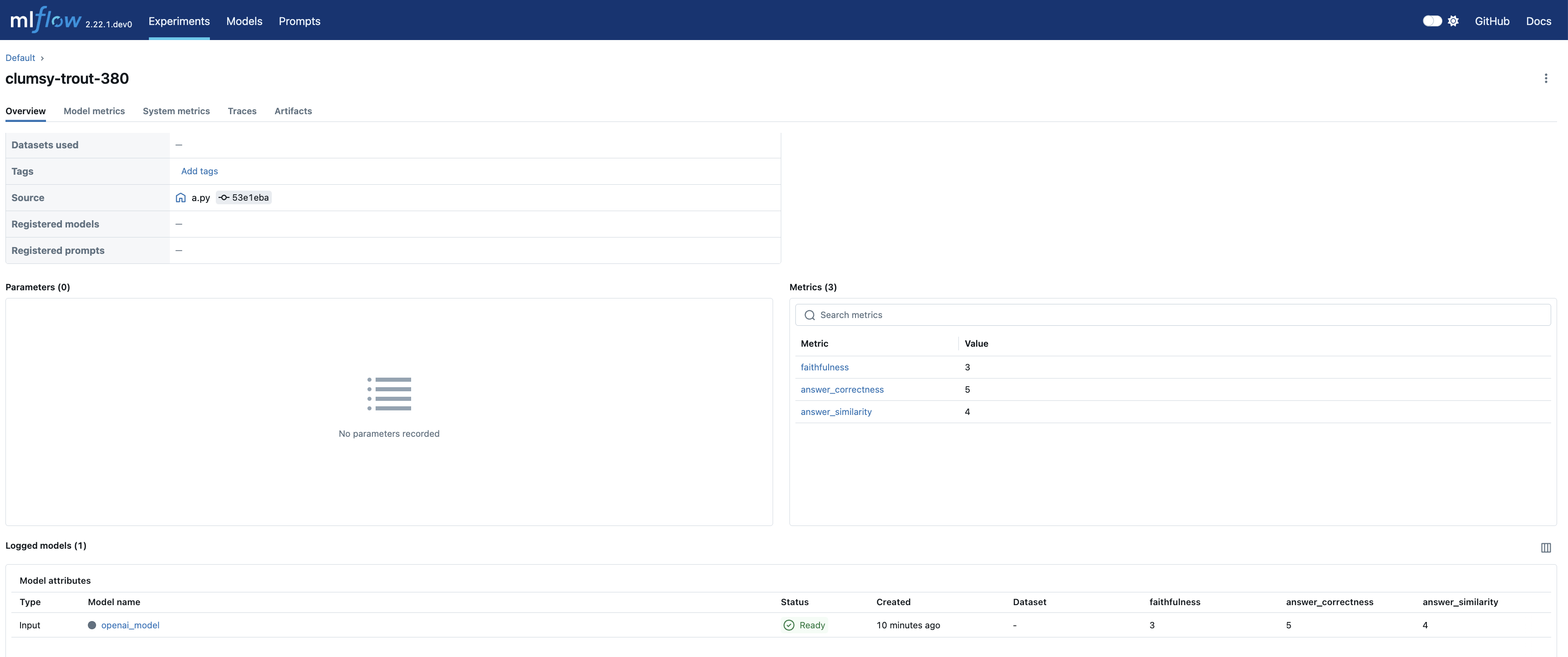
Clicking on the source_run takes you to the evaluation run's page with all the metrics:
MLflow 3 Showcases
Explore the examples below to see how MLflow 3's powerful features can be applied across various domains.
Discover how to log, evaluate, and trace GenAI agents using MLflow 3.
Learn how to leverage MLflow 3 to identify the best models in deep learning workflows.
Migration Guide
MLflow 3 introduces some key API changes while also removes some outdated features. This guide will help you transition smoothly to the latest version.
Key changes
| MLflow 2.x | MLflow 3 | |
|---|---|---|
| log_model API usage | Pass | Pass name when logging a model. This allows you to later search for LoggedModels using this name, note MLflow no longer requires starting a Run before logging models, because Models become
first citizen entity in MLflow 3. You can directly call the |
| Model artifacts storage location | model artifacts are stored as run artifacts. | Model artifacts are stored into models artifacts location. Note: this impacts the behavior of list_artifacts API. |
Removed Features
- MLflow Recipes
- Flavors: the following model flavors are no longer supported
- fastai
- mleap
- AI gateway client APIs: use deployments APIs instead
Breaking changes
Please refer to this page for the full list of breaking changes in MLflow 3.
Compatibility with MLflow 2.x
We strongly recommend upgrading both client and server to MLflow 3.x for the best experience. A mismatch between client and server versions may lead to unexpected behavior.