MLflow for Deep Learning
Deep learning has revolutionized artificial intelligence, enabling breakthrough capabilities in computer vision, natural language processing, generative AI, and countless other domains. As models grow more sophisticated, managing the complexity of deep learning experiments becomes increasingly challenging.
MLflow provides a comprehensive solution for tracking, managing, and deploying deep learning models across all major frameworks. Whether you're fine-tuning transformers, training computer vision models, or developing custom neural networks, MLflow's powerful toolkit simplifies your workflow from experiment to production.
Why Deep Learning Needs MLflow
The Challenges of Modern Deep Learning
- 🔄 Iterative Development: Deep learning requires extensive experimentation with architectures, hyperparameters, and training regimes
- 📊 Complex Metrics: Models generate numerous metrics across training steps that must be tracked and compared
- 💾 Large Artifacts: Models, checkpoints, and visualizations need systematic storage and versioning
- 🧩 Framework Diversity: Teams often work across PyTorch, TensorFlow, Keras, and other specialized libraries
- 🔬 Reproducibility Crisis: Without proper tracking, recreating results becomes nearly impossible
- 👥 Team Collaboration: Multiple researchers need visibility into experiments and the ability to build on each other's work
- 🚀 Deployment Complexities: Moving from successful experiments to production introduces new challenges
MLflow addresses these challenges with a framework-agnostic platform that brings structure and clarity to the entire deep learning lifecycle.
Key Features for Deep Learning
📊 Comprehensive Experiment Tracking
MLflow's tracking capabilities are tailor-made for the iterative nature of deep learning:
- One-Line Autologging for PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Keras
- Step-Based Metrics capture training dynamics across epochs and batches
- Hyperparameter Tracking for architecture choices and training configurations
- Resource Monitoring tracks GPU utilization, memory consumption, and training time
Advanced Tracking Capabilities
Beyond Basic Metrics
MLflow's tracking system supports the specialized needs of deep learning workflows:
- Model Architecture Logging: Automatically capture neural network structures and parameter counts
- Dataset Tracking: Record dataset versions, preprocessing steps, and augmentation parameters
- Visual Debugging: Store sample predictions, attention maps, and other visual artifacts
- Distributed Training: Monitor metrics across multiple nodes in distributed training setups
- Custom Artifacts: Log confusion matrices, embedding projections, and other specialized visualizations
- Hardware Profiling: Track GPU/TPU utilization, memory consumption, and throughput metrics
- Early Stopping Points: Record when early stopping occurred and store the best model states
- Chart Comparison
- Chart Customization
- Run Comparison
- Statistical Evaluation
- Realtime Tracking
- Model Comparison
Compare Training Convergence at a Glance
Visualize multiple deep learning runs to quickly identify which configurations achieve superior performance across training iterations.

Customize Visualizations for Deeper Insights
Tailor charts to focus on critical metrics and training phases, helping you pinpoint exactly when and why certain models outperform others.
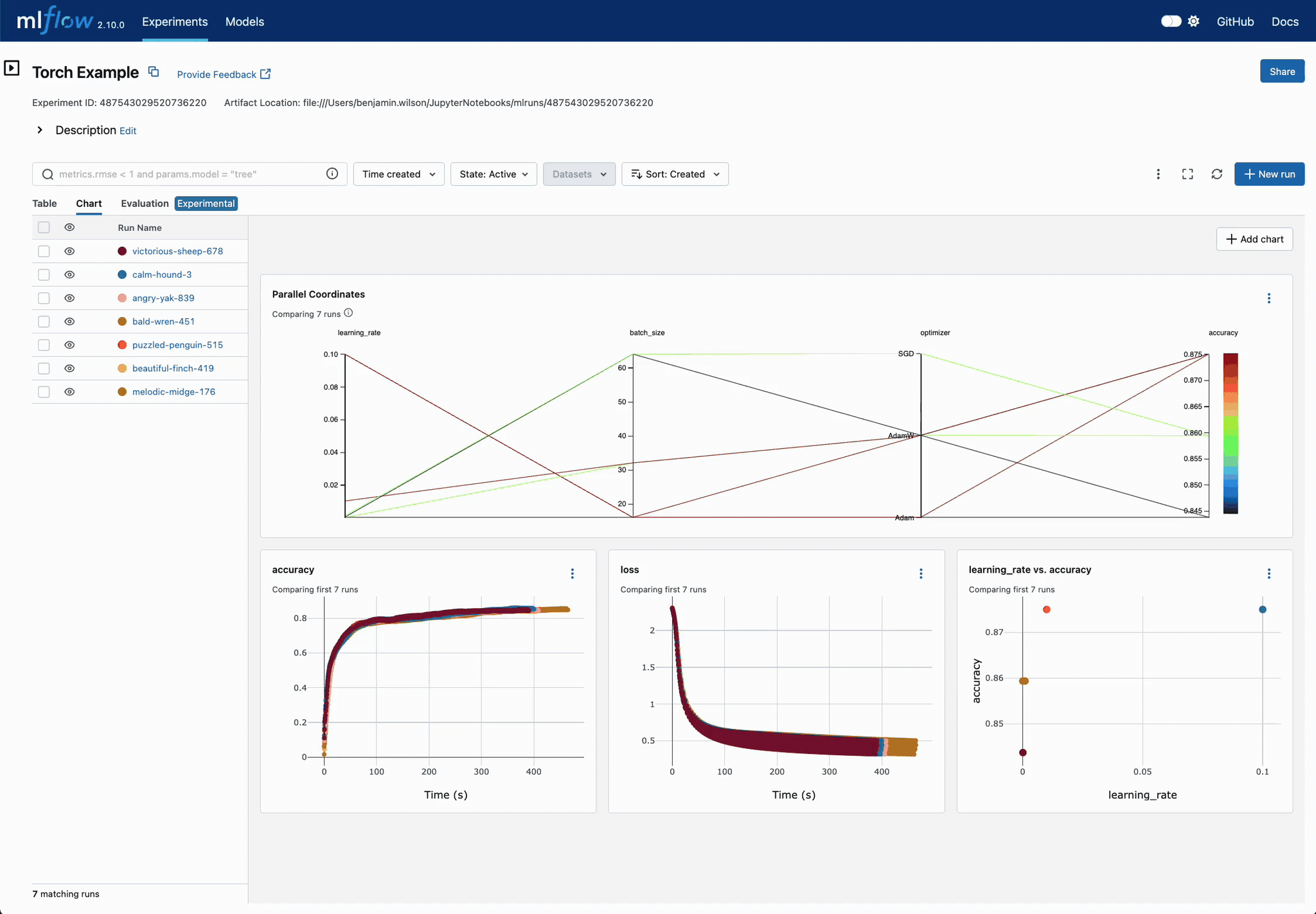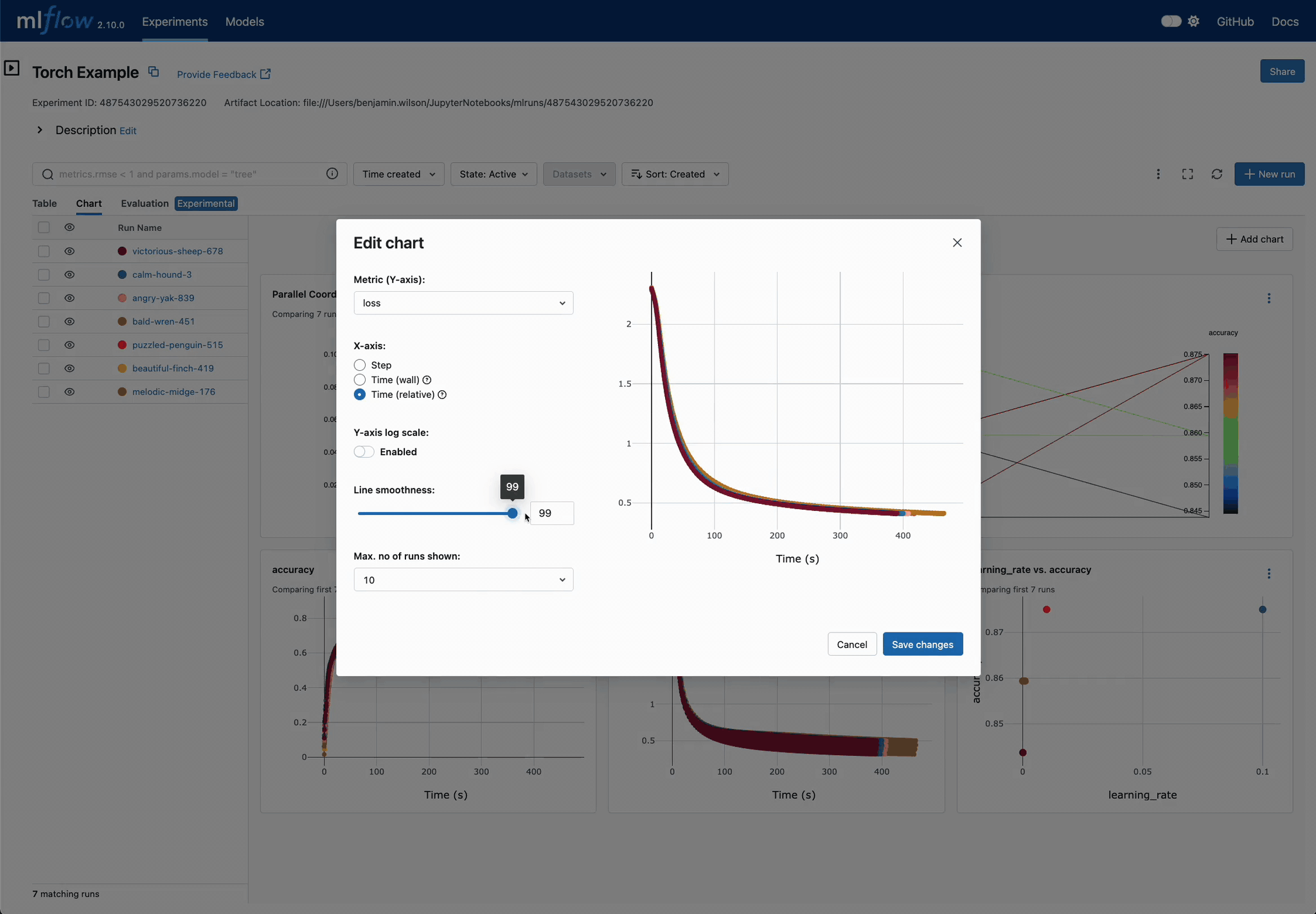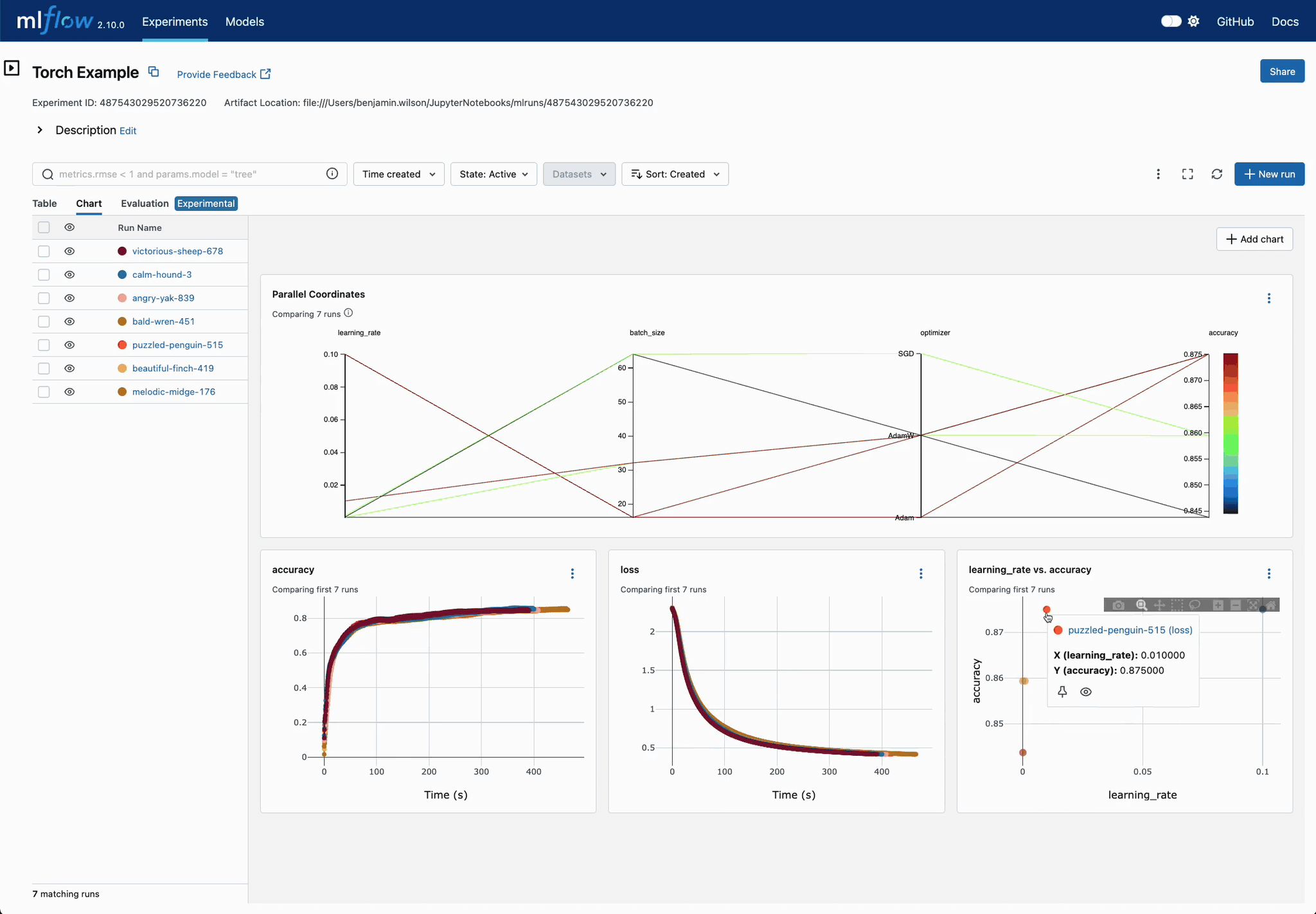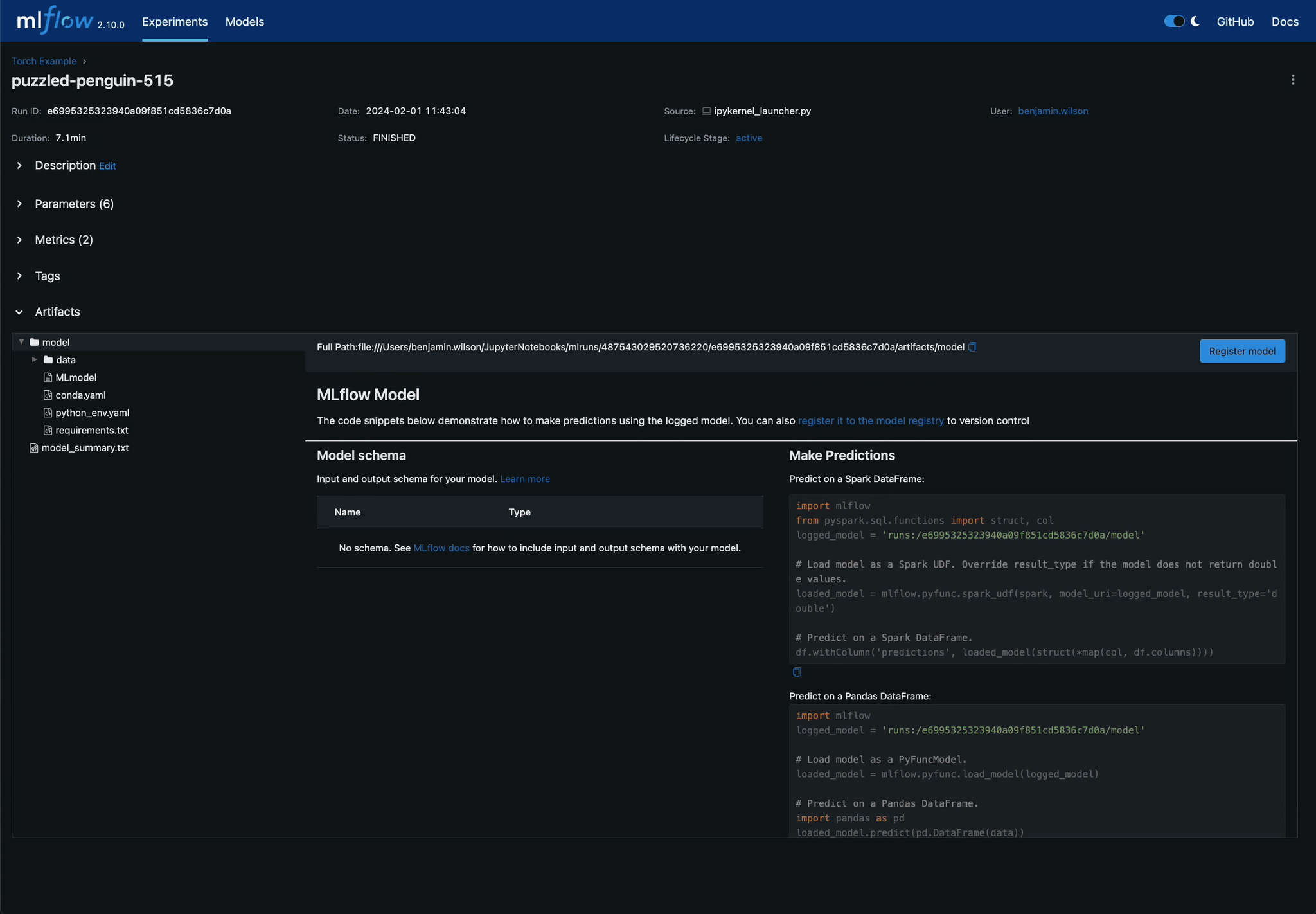
Analyze Parameter Relationships
Explore parameter interactions and their effects on model performance through MLflow's comprehensive comparison views.
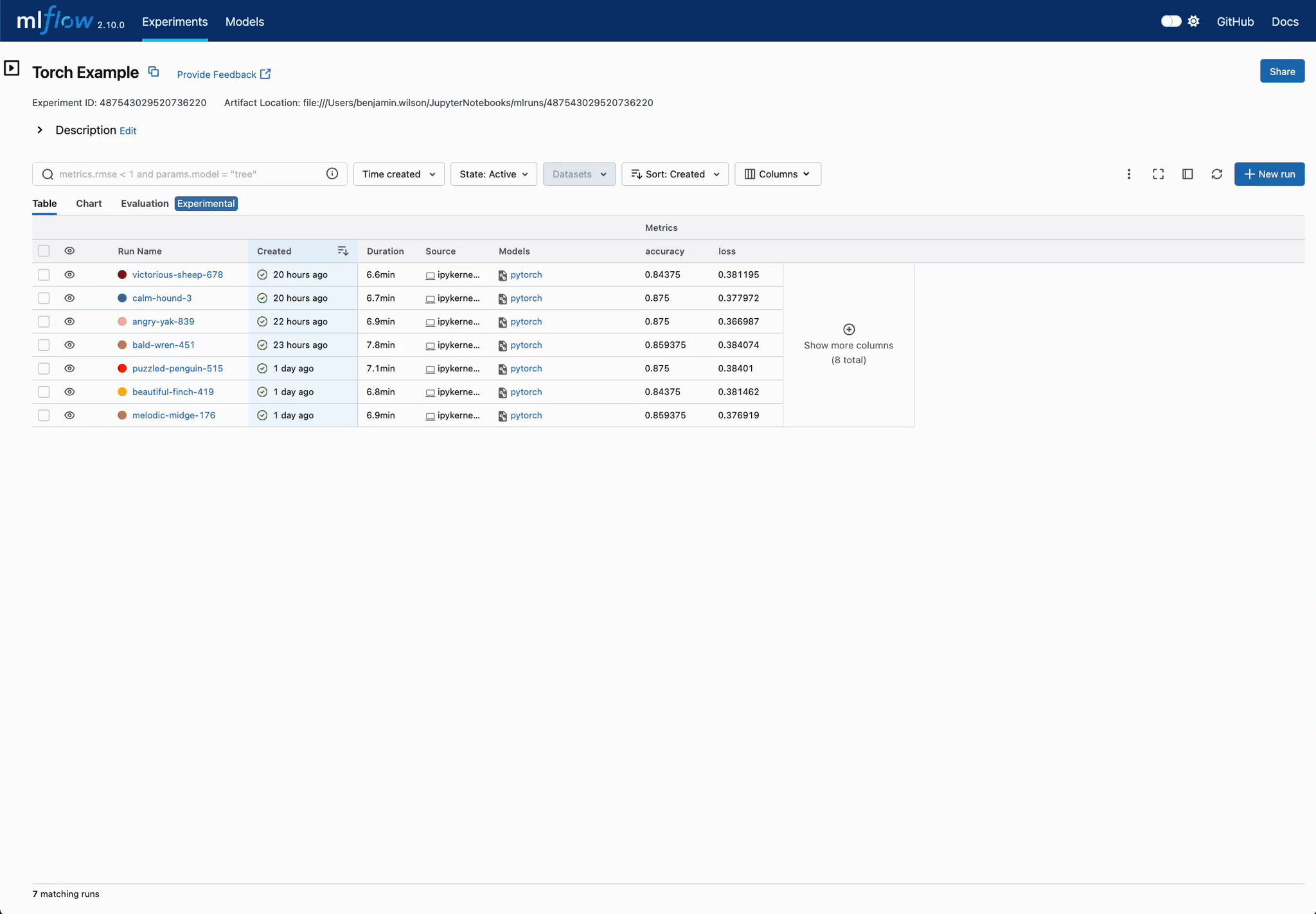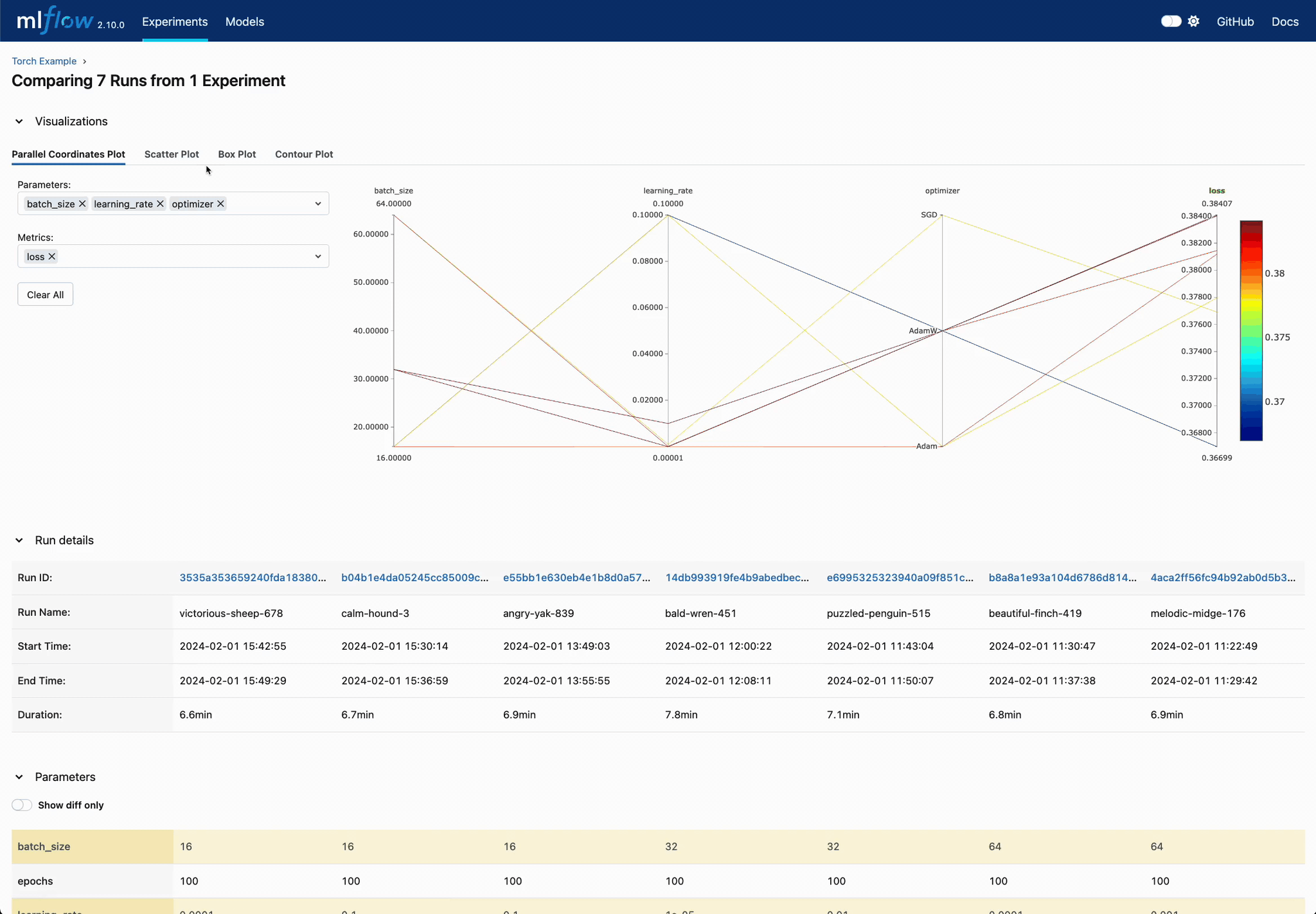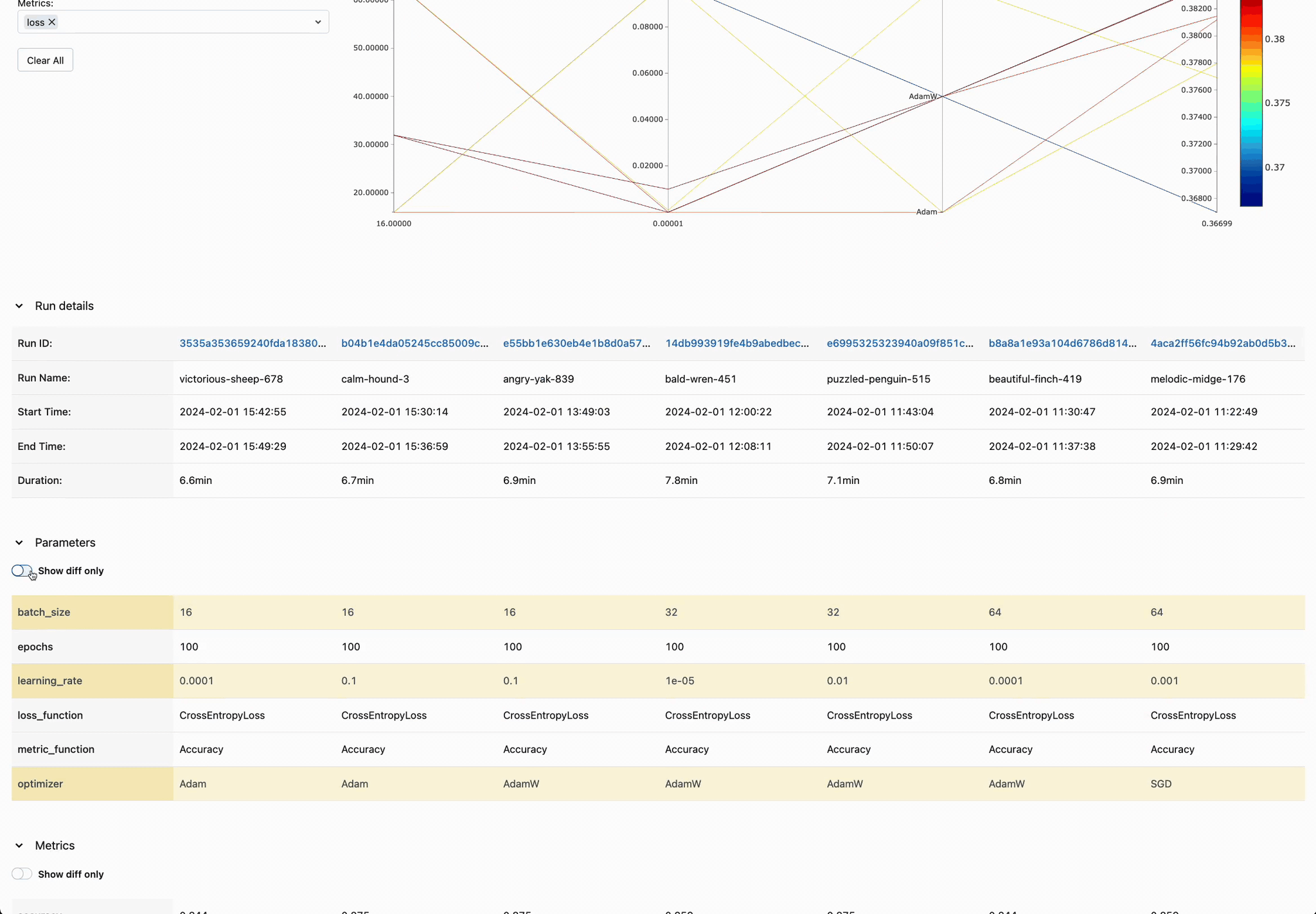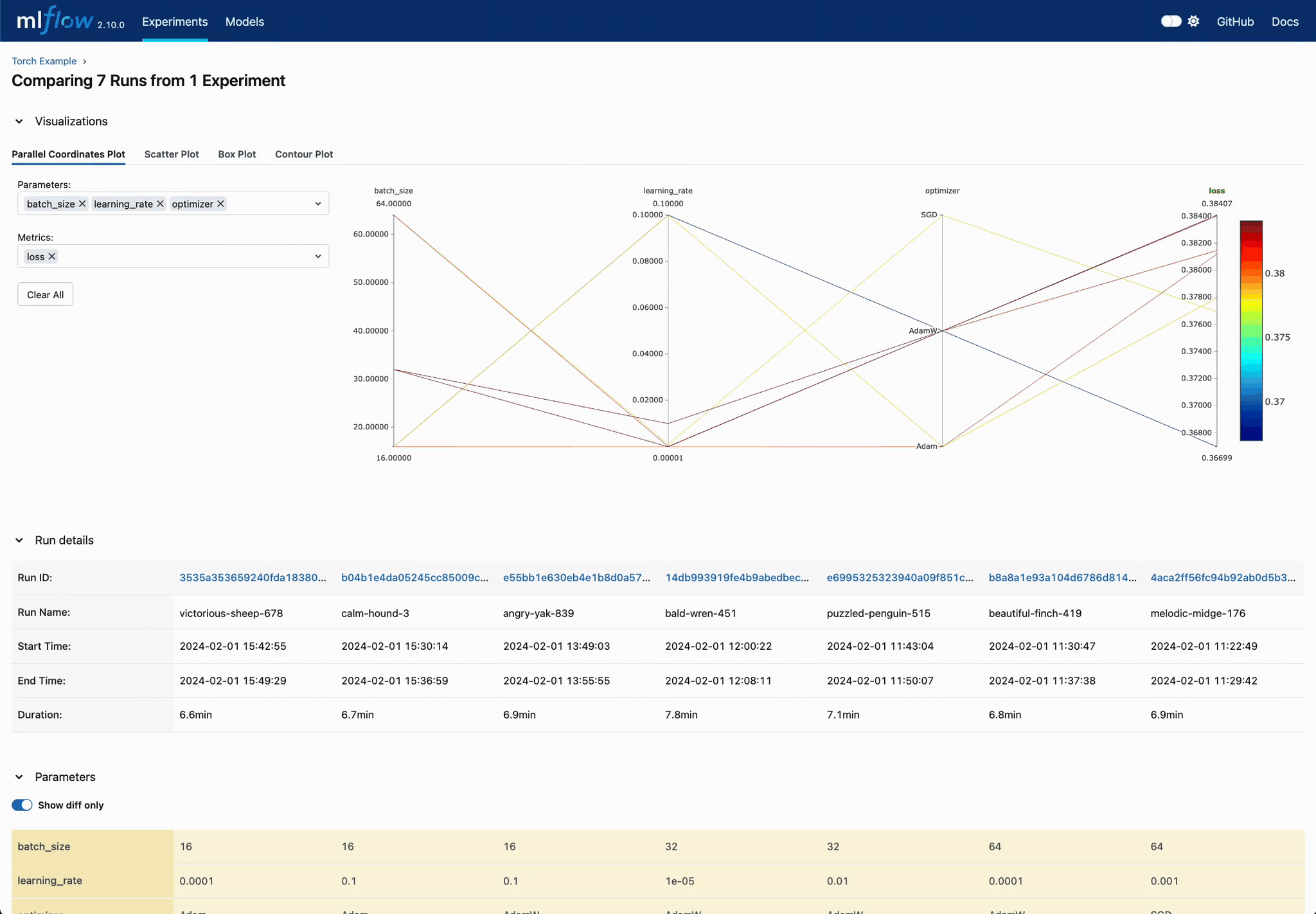
Statistical Insights into Hyperparameters
Use boxplot visualizations to quickly determine which hyperparameter values consistently lead to better performance.
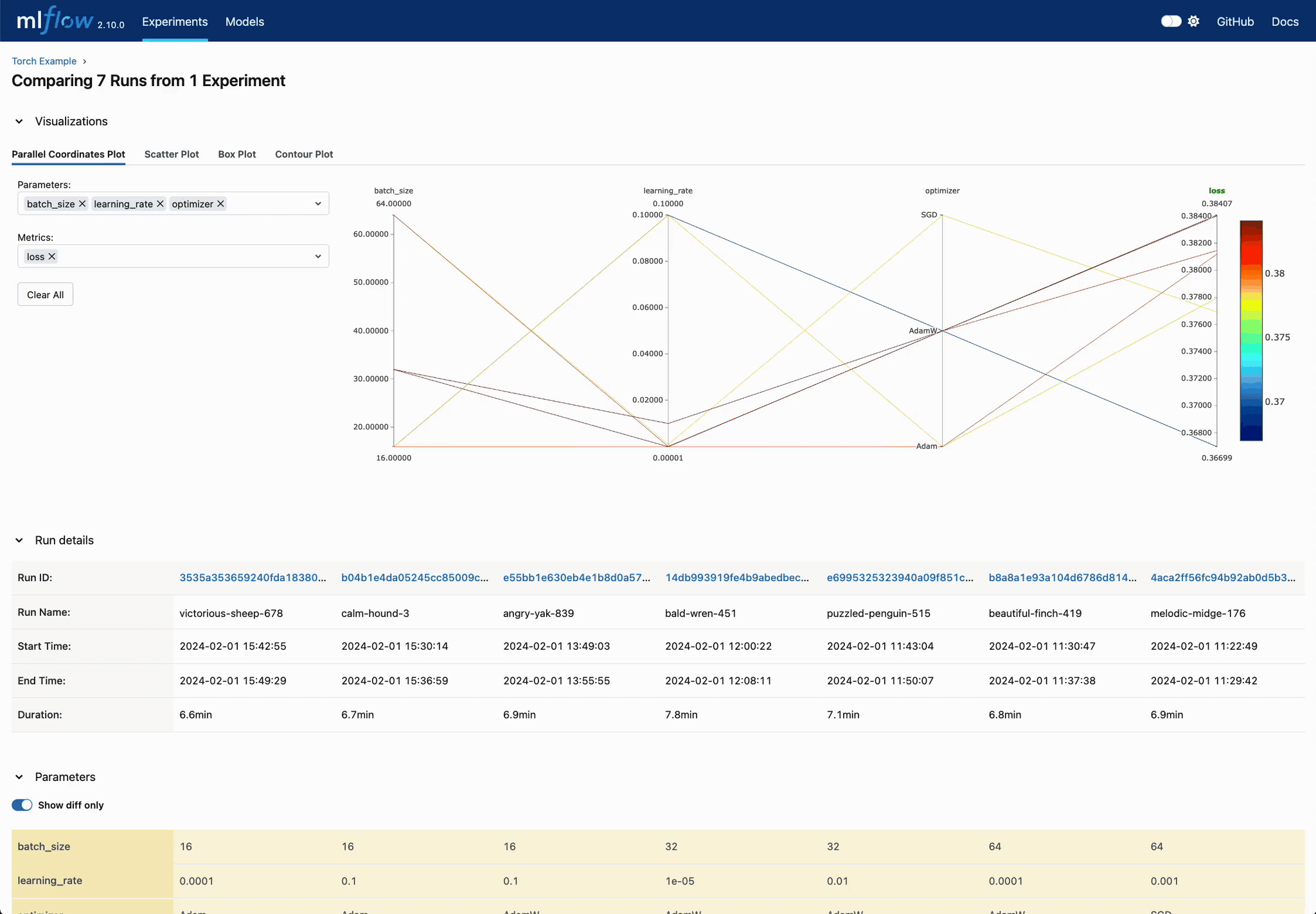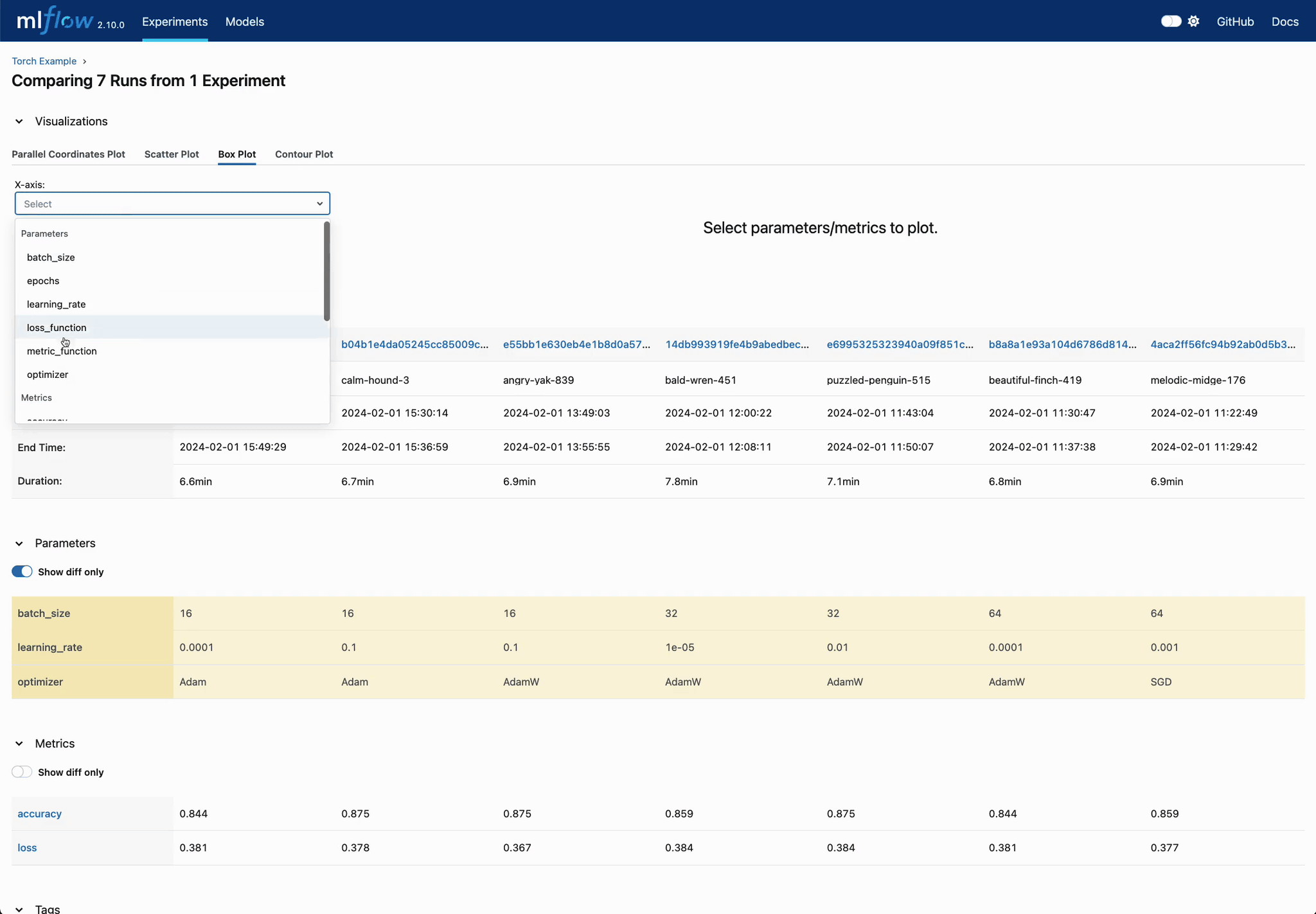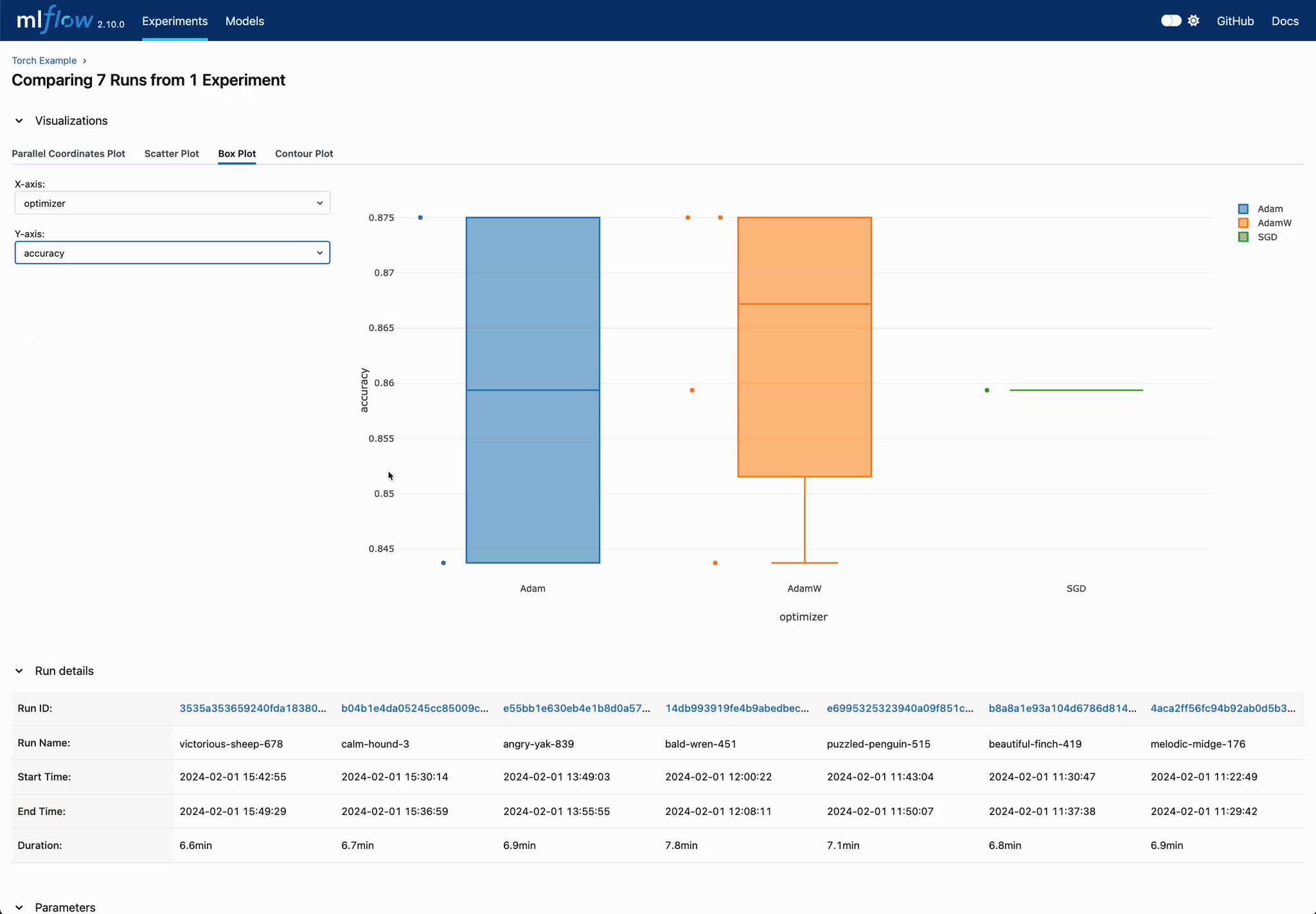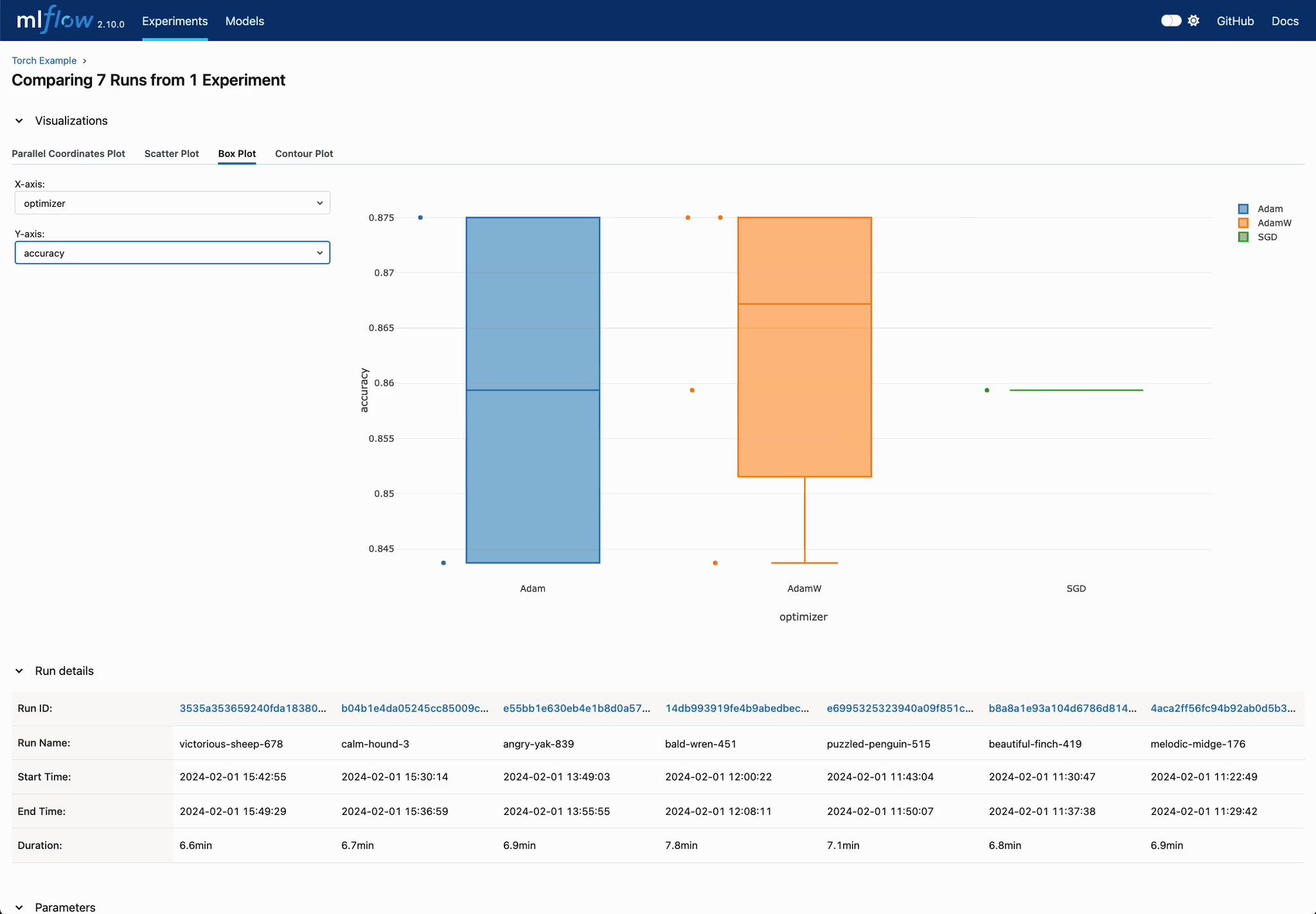
Monitor Training in Real-Time
Watch your deep learning models train with live-updating metrics, eliminating the need for manual progress checks.
![]()
Model Comparison
Track your all your DL checkpoints across epochs using the MLflow UI. Compare performance and quickly find the best checkpoints based on any metrics.
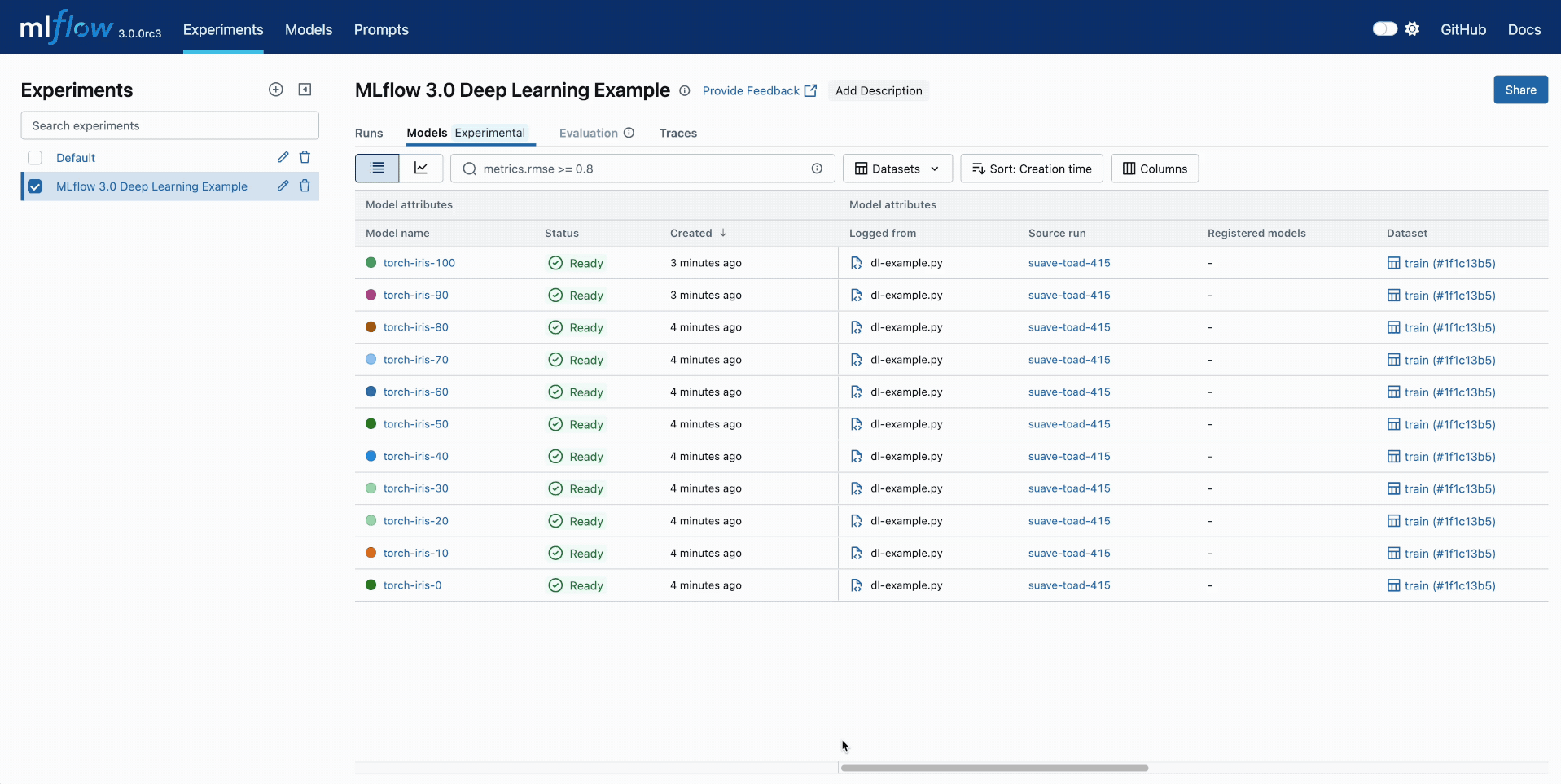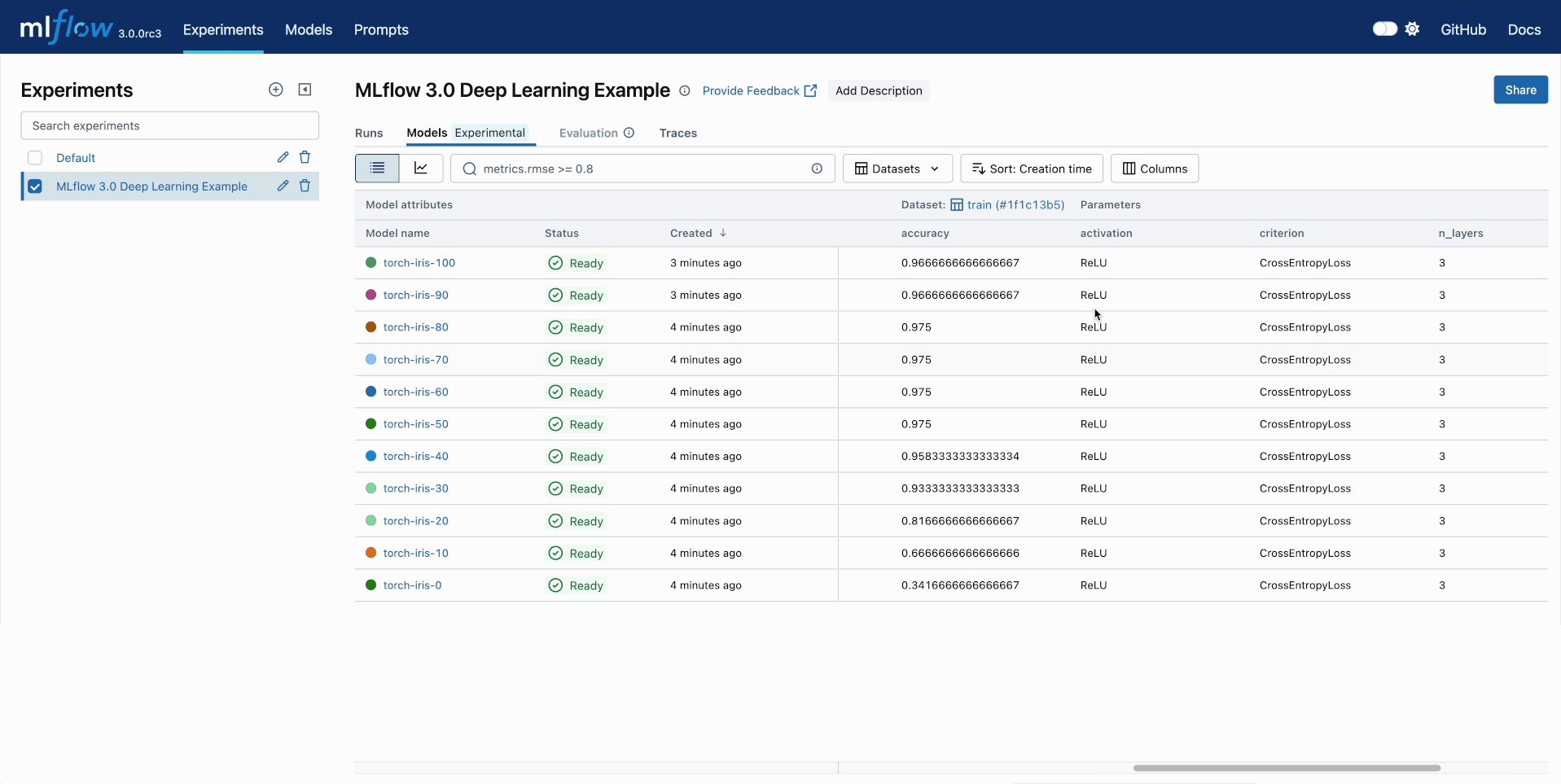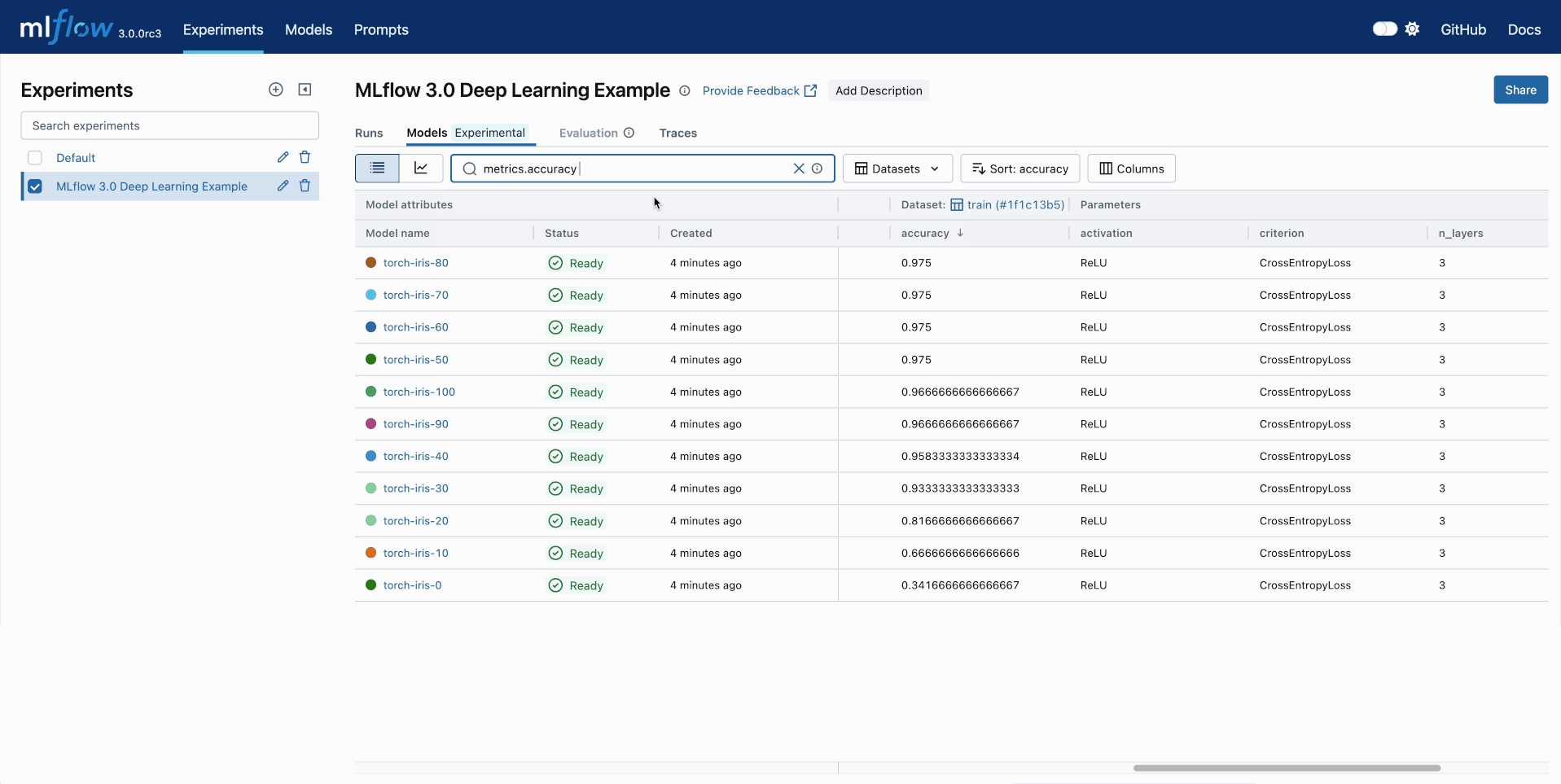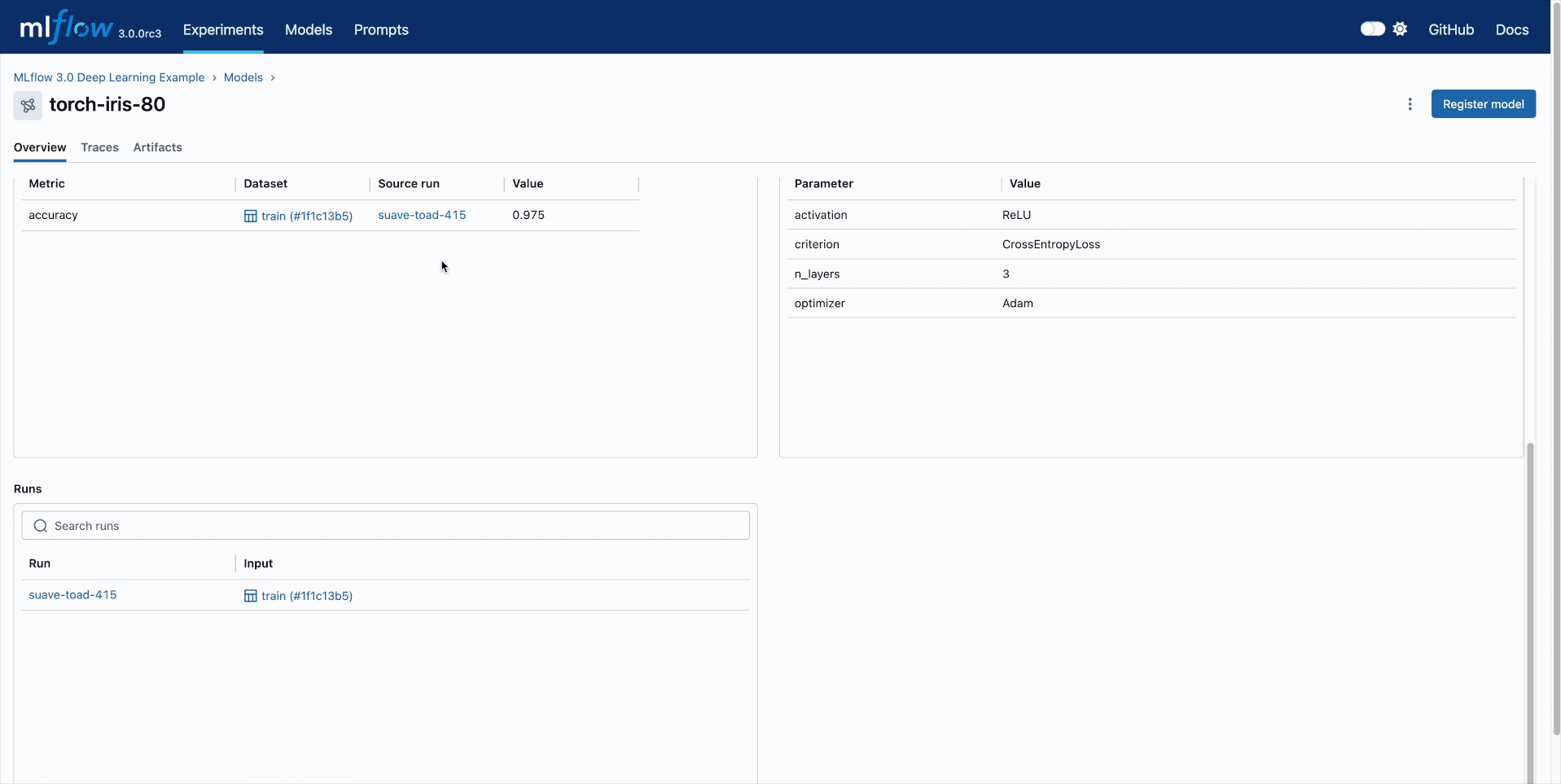
🏆 Streamlined Model Management
Deep learning models are valuable assets that require careful management:
- Versioned Model Registry provides a central repository for all your models
- Model Lineage tracks the complete history from data to deployment
- Metadata Annotations store architecture details, training datasets, and performance metrics
- Stage Transitions manage models through development, staging, and production phases
- Team Permissions control who can view, modify, and deploy models
- Dependency Management ensures all required packages are tracked with the model
Model Registry for Teams
Collaborative Model Development
The MLflow Model Registry enhances team productivity through:
- Transition Requests: Team members can request model promotion with documented justifications
- Approval Workflows: Implement governance with required approvals for production deployments (managed MLflow only)
- Performance Baselines: Set threshold requirements before models can advance to production
- Rollback Capabilities: Quickly revert to previous versions if issues arise
- Activity Feeds: Track who made changes to models and when (managed MLflow only)
- Webhook Integration: Trigger CI/CD pipelines and notifications based on registry events (managed MLflow only)
- Model Documentation: Store comprehensive documentation alongside model artifacts
🚀 Simplified Deployment
Move from successful experiments to production with ease:
- Consistent Inference APIs across all deep learning frameworks
- GPU-Ready Deployments for compute-intensive models
- Batch and Real-Time Serving options for different application needs
- Docker Containerization for portable, isolated environments
- Serverless Deployments for scalable, cost-effective serving within your cloud provider infrastructure
- Edge Deployment support for mobile and IoT applications
Advanced Deployment Options
Beyond Basic Serving
MLflow supports sophisticated deployment scenarios for deep learning:
- Model Ensembling: Deploy multiple models with voting or averaging mechanisms
- Custom Preprocessing/Postprocessing: Attach data transformation pipelines to your model
- Optimized Inference: Support for quantization, pruning, and other optimization techniques
- Monitoring Integration: Connect to observability platforms for production tracking
- Hardware Acceleration: Leverage GPU/TPU resources for high-throughput inference in cloud provider infrastructure
- Scalable Architecture: Handle variable loads with auto-scaling capabilities (managed MLflow only)
- Multi-Framework Deployment: Mix models from different frameworks in the same serving environment
Framework Integrations
MLflow provides native support for all major deep learning frameworks, allowing you to use your preferred tools while gaining the benefits of unified experiment tracking and model management.
Seamlessly track TensorFlow experiments with one-line autologging. Capture training metrics, model architecture, and TensorBoard visualizations in a centralized repository.
Integrate MLflow with PyTorch's flexible deep learning ecosystem. Log metrics from custom training loops, save model checkpoints, and simplify deployment for production.
Harness Keras 3.0's multi-backend capabilities with comprehensive MLflow tracking. Monitor training across TensorFlow, PyTorch, and JAX backends with consistent experiment management.
Track and manage spaCy NLP models throughout their lifecycle. Log training metrics, compare model versions, and deploy language processing pipelines to production.
Getting Started
Quick Setup Guide
1. Install MLflow
pip install mlflow
Ensure that you have the appropriate DL integration package installed. For example, for PyTorch with image model support:
pip install torch torchvision
2. Start Tracking Server (Optional)
# Start a local tracking server
mlflow server --host 0.0.0.0 --port 5000
3. Enable Autologging
import mlflow
# For TensorFlow/Keras
mlflow.tensorflow.autolog()
# For PyTorch Lightning
mlflow.pytorch.autolog()
# For all supported frameworks
mlflow.autolog()
4. Train Your Model Normally
# Your existing training code works unchanged!
model.fit(train_data, train_labels, epochs=10, validation_data=(val_data, val_labels))
5. View Results
Open the MLflow UI to see your tracked experiments:
mlflow ui
Or if using a tracking server:
http://localhost:5000
Real-World Applications
Deep learning with MLflow powers a wide range of applications across industries:
- 🖼️ Computer Vision: Track performance of object detection, image segmentation, and classification models
- 🔊 Speech Recognition: Monitor acoustic model training and compare word error rates across architectures
- 📝 Natural Language Processing: Manage fine-tuning of large language models and evaluate performance on downstream tasks
- 🎮 Reinforcement Learning: Track agent performance, rewards, and environmental interactions across training runs
- 🧬 Genomics: Organize deep learning models analyzing genetic sequences and protein structures
- 📊 Financial Forecasting: Compare predictive models for time series analysis and risk assessment
- 🏭 Manufacturing: Deploy computer vision models for quality control and predictive maintenance
- 🏥 Healthcare: Manage medical imaging models with rigorous versioning and approval workflows
Advanced Topics
Distributed Training Integration
MLflow integrates seamlessly with distributed training frameworks:
- Horovod: Track metrics across distributed TensorFlow and PyTorch training
- PyTorch DDP: Monitor distributed data parallel training
- TensorFlow Distribution Strategies: Log metrics from multi-GPU and multi-node training
- Ray: Integrate with Ray's distributed computing ecosystem
Example with PyTorch DDP:
import mlflow
import torch.distributed as dist
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel
mlflow.pytorch.autolog()
# Initialize process group
dist.init_process_group(backend="nccl")
# Create model and move to GPU with DDP wrapper
model = DistributedDataParallel(model.to(rank))
# MLflow tracking works normally with DDP
with mlflow.start_run():
trainer.fit(model)
Hyperparameter Optimization
MLflow integrates with popular hyperparameter optimization frameworks:
- Optuna: Track trials and visualize optimization results
- Ray Tune: Monitor distributed hyperparameter sweeps
- Weights & Biases Sweeps: Synchronize W&B sweeps with MLflow tracking
- HyperOpt: Organize and compare hyperparameter search results
Example with Optuna:
import mlflow
import optuna
def objective(trial):
with mlflow.start_run(nested=True):
# Suggest hyperparameters
lr = trial.suggest_float("lr", 1e-5, 1e-1, log=True)
batch_size = trial.suggest_categorical("batch_size", [16, 32, 64, 128])
# Log parameters to MLflow
mlflow.log_params({"lr": lr, "batch_size": batch_size})
# Train model
model = create_model(lr)
result = train_model(model, batch_size)
# Log results
mlflow.log_metrics({"accuracy": result["accuracy"]})
return result["accuracy"]
# Create study
with mlflow.start_run():
study = optuna.create_study(direction="maximize")
study.optimize(objective, n_trials=100)
# Log best parameters
mlflow.log_params({f"best_{k}": v for k, v in study.best_params.items()})
mlflow.log_metric("best_accuracy", study.best_value)
Transfer Learning Workflows
MLflow helps organize transfer learning and fine-tuning workflows:
- Base Model Registry: Maintain a catalog of pre-trained models
- Fine-Tuning Tracking: Monitor performance as you adapt models to new tasks
- Layer Freezing Analysis: Compare different layer freezing strategies
- Learning Rate Scheduling: Track the impact of different learning rate strategies for fine-tuning
Example tracking a fine-tuning run:
import mlflow
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
with mlflow.start_run():
# Log base model information
base_model_name = "bert-base-uncased"
mlflow.log_param("base_model", base_model_name)
# Create and customize model for fine-tuning
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(base_model_name)
# Log which layers are frozen
frozen_layers = ["embeddings", "encoder.layer.0", "encoder.layer.1"]
mlflow.log_param("frozen_layers", frozen_layers)
# Freeze specified layers
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if any(layer in name for layer in frozen_layers):
param.requires_grad = False
# Log trainable parameter count
trainable_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
mlflow.log_params(
{
"trainable_params": trainable_params,
"total_params": total_params,
"trainable_percentage": trainable_params / total_params,
}
)
# Fine-tune and track results...
Learn More
Dive deeper into MLflow's capabilities for deep learning in our framework-specific guides:
- TensorFlow Guide: Master MLflow's integration with TensorFlow and Keras
- PyTorch Guide: Learn how to track custom PyTorch training loops
- Keras Guide: Explore Keras 3.0's multi-backend capabilities with MLflow
- Model Registry: Manage model versions and transitions through development stages
- MLflow Deployments: Deploy deep learning models to production