Setting Trace Tags
Tags are mutable key-value pairs that you can attach to traces to add valuable metadata and context. This metadata is useful for organizing, searching, and filtering your traces. For example, you might tag your traces based on the topic of the user's input, the environment they're running in, or the model version being used.
MLflow provides the flexibility to add, update, or remove tags at any point—even after a trace is logged—through its APIs or the MLflow UI.
When to Use Trace Tags
Trace tags are particularly useful for:
- Session Management: Group traces by conversation sessions or user interactions
- Environment Tracking: Distinguish between production, staging, and development traces
- Model Versioning: Track which model version generated specific traces
- User Context: Associate traces with specific users or customer segments
- Performance Monitoring: Tag traces based on performance characteristics
- A/B Testing: Differentiate between different experimental variants
- Active Traces
- Finished Traces
- Search & Filter
- Best Practices
Setting Tags on Active Traces
Use mlflow.update_current_trace() to add tags during trace execution.
import mlflow
@mlflow.trace
def my_func(x):
mlflow.update_current_trace(tags={"fruit": "apple"})
return x + 1
result = my_func(5)
Example: Setting Service Tags in Production System
import mlflow
import os
@mlflow.trace
def process_user_request(user_id: str, session_id: str, request_text: str):
# Add comprehensive tags for production monitoring
mlflow.update_current_trace(
tags={
"user_id": user_id,
"session_id": session_id,
"environment": os.getenv("ENVIRONMENT", "development"),
"model_version": os.getenv("MODEL_VERSION", "1.0.0"),
"request_type": "chat_completion",
"priority": "high" if "urgent" in request_text.lower() else "normal",
}
)
response = f"Processed: {request_text}"
return response
The mlflow.update_current_trace() function adds the specified tag(s) to the current trace when the key is not already present. If the key is already present, it updates the key with the new value.
Setting Tags on Finished Traces
Add or modify tags on traces that have already been completed and logged.
Available APIs
| API | Use Case |
|---|---|
mlflow.set_trace_tag() | Fluent API for setting tags |
mlflow.client.MlflowClient.set_trace_tag() | Client API for setting tags |
| MLflow UI | Visual tag management |
Basic Usage
import mlflow
from mlflow import MlflowClient
# Using fluent API
mlflow.set_trace_tag(trace_id="your-trace-id", key="tag_key", value="tag_value")
mlflow.delete_trace_tag(trace_id="your-trace-id", key="tag_key")
# Using client API
client = MlflowClient()
client.set_trace_tag(trace_id="your-trace-id", key="tag_key", value="tag_value")
client.delete_trace_tag(trace_id="your-trace-id", key="tag_key")
Batch Tagging
import mlflow
from mlflow import MlflowClient
client = MlflowClient()
# Find traces that need to be tagged
traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="status = 'ERROR'", max_results=100
)
# Add tags to all error traces
for trace in traces:
client.set_trace_tag(trace_id=trace.info.trace_id, key="needs_review", value="true")
client.set_trace_tag(
trace_id=trace.info.trace_id, key="review_priority", value="high"
)
Performance Analysis Tagging
import mlflow
from mlflow import MlflowClient
from datetime import datetime
client = MlflowClient()
# Get slow traces for analysis
traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="execution_time_ms > 5000", max_results=50
)
# Tag based on performance analysis
for trace in traces:
execution_time = trace.info.execution_time_ms
if execution_time > 10000:
performance_tag = "very_slow"
elif execution_time > 7500:
performance_tag = "slow"
else:
performance_tag = "moderate"
client.set_trace_tag(
trace_id=trace.info.trace_id, key="performance_category", value=performance_tag
)
Using the MLflow UI
Navigate to the trace details page and click the pencil icon next to tags to edit them visually.
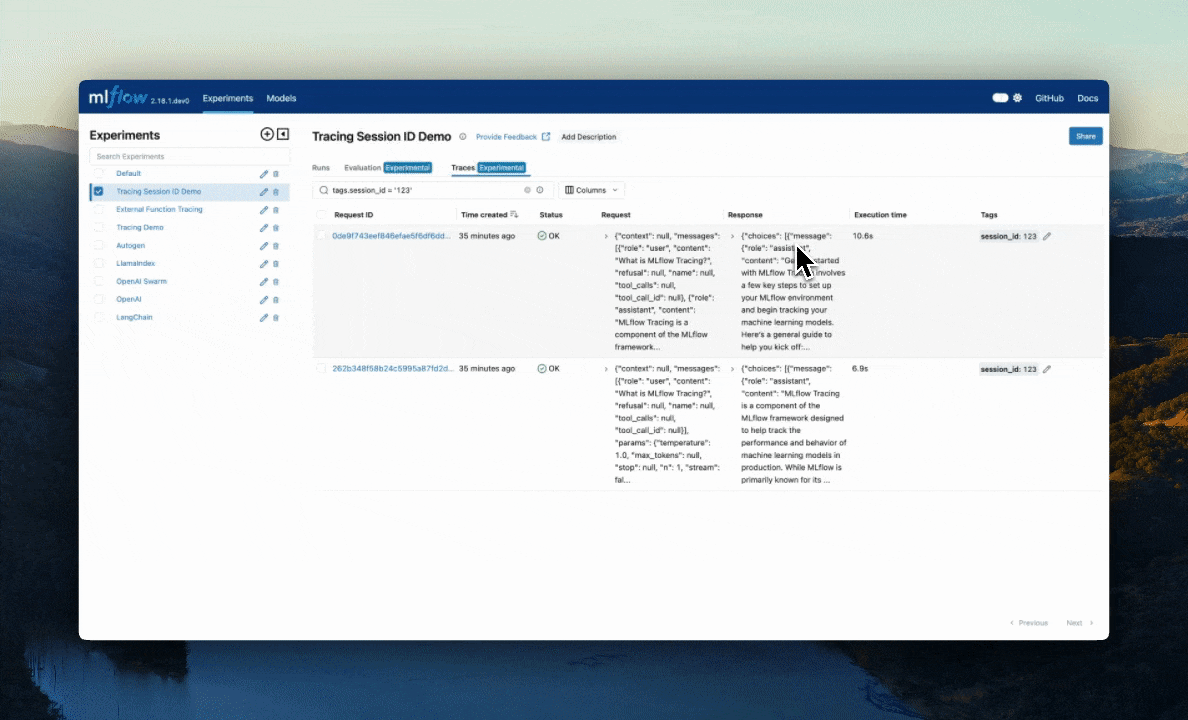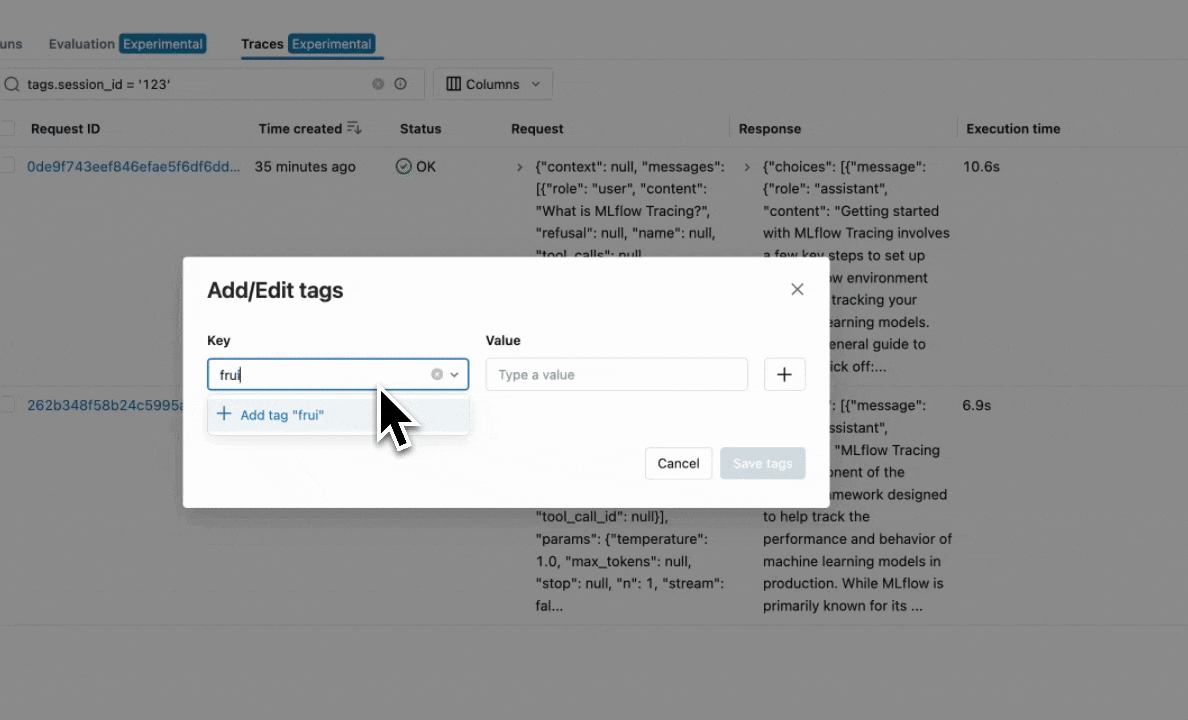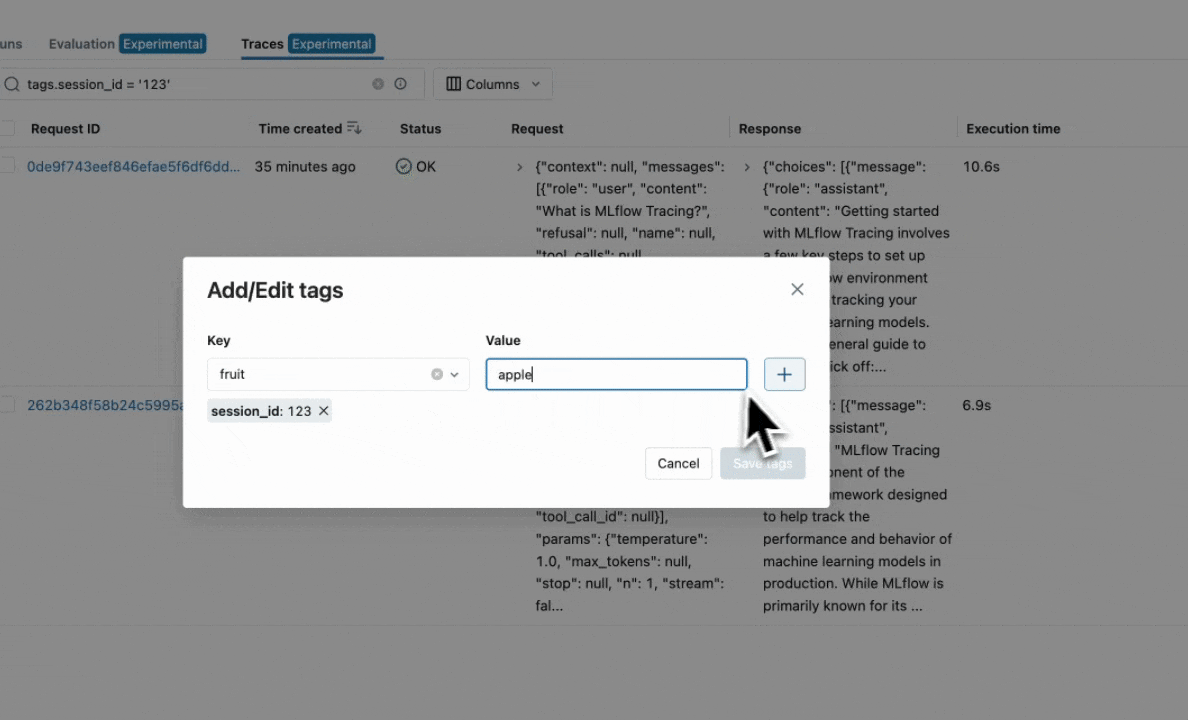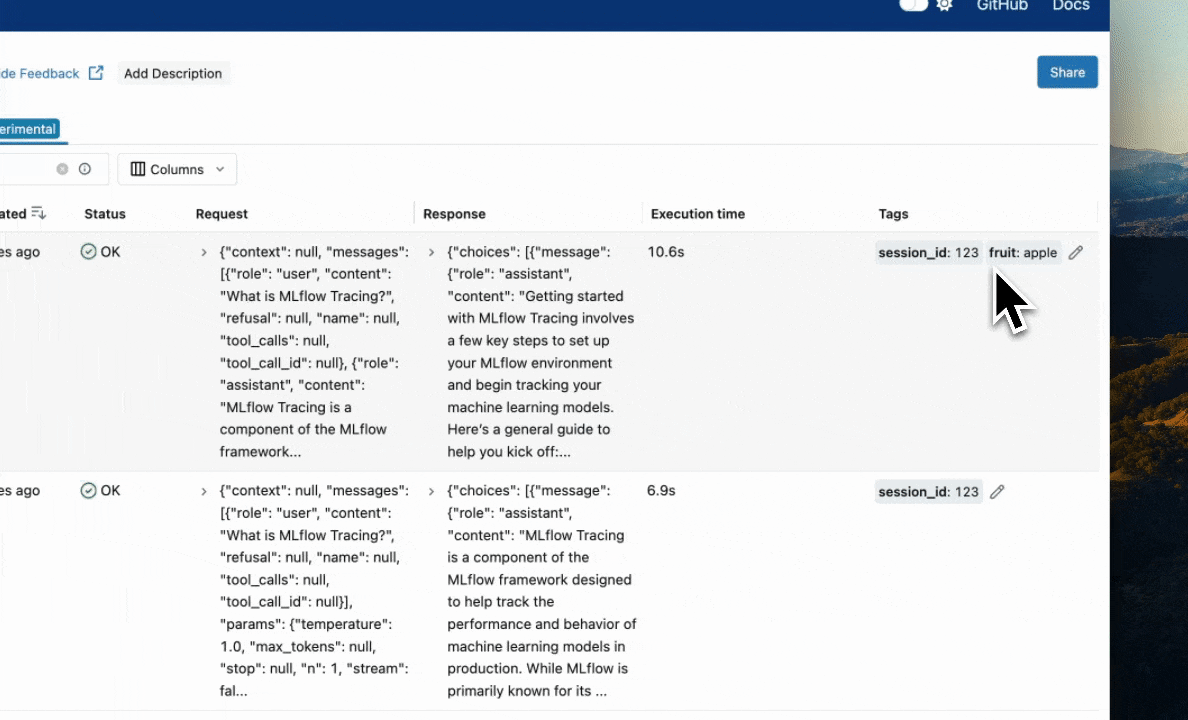
UI capabilities:
- Add new tags by clicking the "+" button
- Edit existing tags by clicking the pencil icon
- Delete tags by clicking the trash icon
- View all tags associated with a trace
Searching and Filtering with Tags
Use tags to find specific traces quickly and efficiently.
Basic Tag Filtering
import mlflow
# Find traces by environment
production_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.environment = 'production'"
)
# Find traces by user
user_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.user_id = 'user_123'"
)
# Find high-priority traces
urgent_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.priority = 'high'"
)
Complex Tag-Based Queries
# Combine tag filters with other conditions
slow_production_errors = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"],
filter_string="""
tags.environment = 'production'
AND status = 'ERROR'
AND execution_time_ms > 5000
""",
)
# Find traces that need review
review_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"],
filter_string="tags.needs_review = 'true'",
order_by=["timestamp_ms DESC"],
)
# Find specific user sessions
session_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"],
filter_string="tags.session_id = 'session_456'",
order_by=["timestamp_ms ASC"],
)
Operational Monitoring Queries
# Monitor A/B test performance
control_group = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.experiment_variant = 'control'"
)
treatment_group = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.experiment_variant = 'treatment'"
)
# Find traces needing escalation
escalation_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"],
filter_string="""
tags.sla_tier = 'critical'
AND execution_time_ms > 30000
""",
)
Analytics and Reporting
# Generate performance reports by model version
model_v1_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.model_version = 'v1.0.0'"
)
model_v2_traces = mlflow.search_traces(
experiment_ids=["1"], filter_string="tags.model_version = 'v2.0.0'"
)
# Compare performance
v1_avg_time = sum(t.info.execution_time_ms for t in model_v1_traces) / len(
model_v1_traces
)
v2_avg_time = sum(t.info.execution_time_ms for t in model_v2_traces) / len(
model_v2_traces
)
print(f"V1 average time: {v1_avg_time:.2f}ms")
print(f"V2 average time: {v2_avg_time:.2f}ms")
Best Practices for Trace Tags
1. Consistent Naming Conventions
# Good: Consistent naming
tags = {
"environment": "production", # lowercase
"model_version": "v2.1.0", # semantic versioning
"user_segment": "premium", # descriptive names
"processing_stage": "preprocessing", # clear context
}
# Avoid: Inconsistent naming
tags = {
"env": "PROD", # abbreviation + uppercase
"ModelVer": "2.1", # mixed case + different format
"user_type": "premium", # different terminology
"stage": "pre", # unclear abbreviation
}
2. Hierarchical Organization
# Use dots for hierarchical organization
tags = {
"service.name": "chat_api",
"service.version": "1.2.0",
"service.region": "us-east-1",
"user.segment": "enterprise",
"user.plan": "premium",
"request.type": "completion",
"request.priority": "high",
}
3. Temporal Information
import datetime
tags = {
"deployment_date": "2024-01-15",
"quarter": "Q1_2024",
"week": "2024-W03",
"shift": "evening", # for operational monitoring
}
4. Operational Monitoring
# Tags for monitoring and alerting
tags = {
"sla_tier": "critical", # for SLA monitoring
"cost_center": "ml_platform", # for cost attribution
"alert_group": "ml_ops", # for alert routing
"escalation": "tier_1", # for incident management
}
5. Experiment Tracking
# Tags for A/B testing and experiments
tags = {
"experiment_name": "prompt_optimization_v2",
"variant": "control",
"hypothesis": "improved_context_helps",
"feature_flag": "new_prompt_engine",
}
Common Tag Categories
| Category | Example Tags | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | environment: production/staging/dev | Deployment tracking |
| User Context | user_id, session_id, user_segment | User behavior analysis |
| Model Info | model_version, model_type, checkpoint | Model performance tracking |
| Request Type | request_type, complexity, priority | Request categorization |
| Performance | latency_tier, cost_category, sla_tier | Performance monitoring |
| Business Logic | feature_flag, experiment_variant, routing | A/B testing and routing |
| Operational | region, deployment_id, instance_type | Infrastructure tracking |
Tag Naming Guidelines
- Use lowercase with underscores for consistency
- Be descriptive but concise
- Use semantic versioning for versions (v1.2.3)
- Include units when relevant (time_seconds, size_mb)
- Use hierarchical naming for related concepts (service.name, service.version)
- Avoid abbreviations unless they're well-known in your domain
Summary
Trace tags provide a powerful way to add context and metadata to your MLflow traces, enabling:
- Better Organization: Group related traces together
- Powerful Filtering: Find specific traces quickly using search
- Operational Monitoring: Track performance and issues by category
- User Analytics: Understand user behavior patterns
- Debugging: Add context that helps with troubleshooting
Whether you're adding tags during trace execution or after the fact, tags make your tracing data more valuable and actionable for production monitoring and analysis.