Tracing DeepSeek
MLflow Tracing provides automatic tracing capability for Deepseek models through the OpenAI SDK integration. Since DeepSeek uses an OpenAI-compatible API format, you can use mlflow.openai.autolog() to trace interactions with DeepSeek models.
import mlflow
# Enable
mlflow.openai.autolog()
MLflow trace automatically captures the following information about DeepSeek calls:
- Prompts and completion responses
- Latencies
- Model name
- Additional metadata such as
temperature,max_tokens, if specified. - Function calling if returned in the response
- Any exception if raised
Supported APIs
MLflow supports automatic tracing for the following DeepSeek APIs through the OpenAI integration:
| Chat Completion | Function Calling | Streaming | Async |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | ✅ (*1) | ✅ (*2) |
(*1) Streaming support requires MLflow 2.15.0 or later. (*2) Async support requires MLflow 2.21.0 or later.
To request support for additional APIs, please open a feature request on GitHub.
Basic Example
import openai
import mlflow
# Enable auto-tracing for OpenAI (works with DeepSeek)
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Optional: Set a tracking URI and an experiment
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("http://localhost:5000")
mlflow.set_experiment("DeepSeek")
# Initialize the OpenAI client with DeepSeek API endpoint
client = openai.OpenAI(
base_url="https://api.deepseek.com", api_key="<your_deepseek_api_key>"
)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the capital of France?"},
]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=messages,
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=100,
)
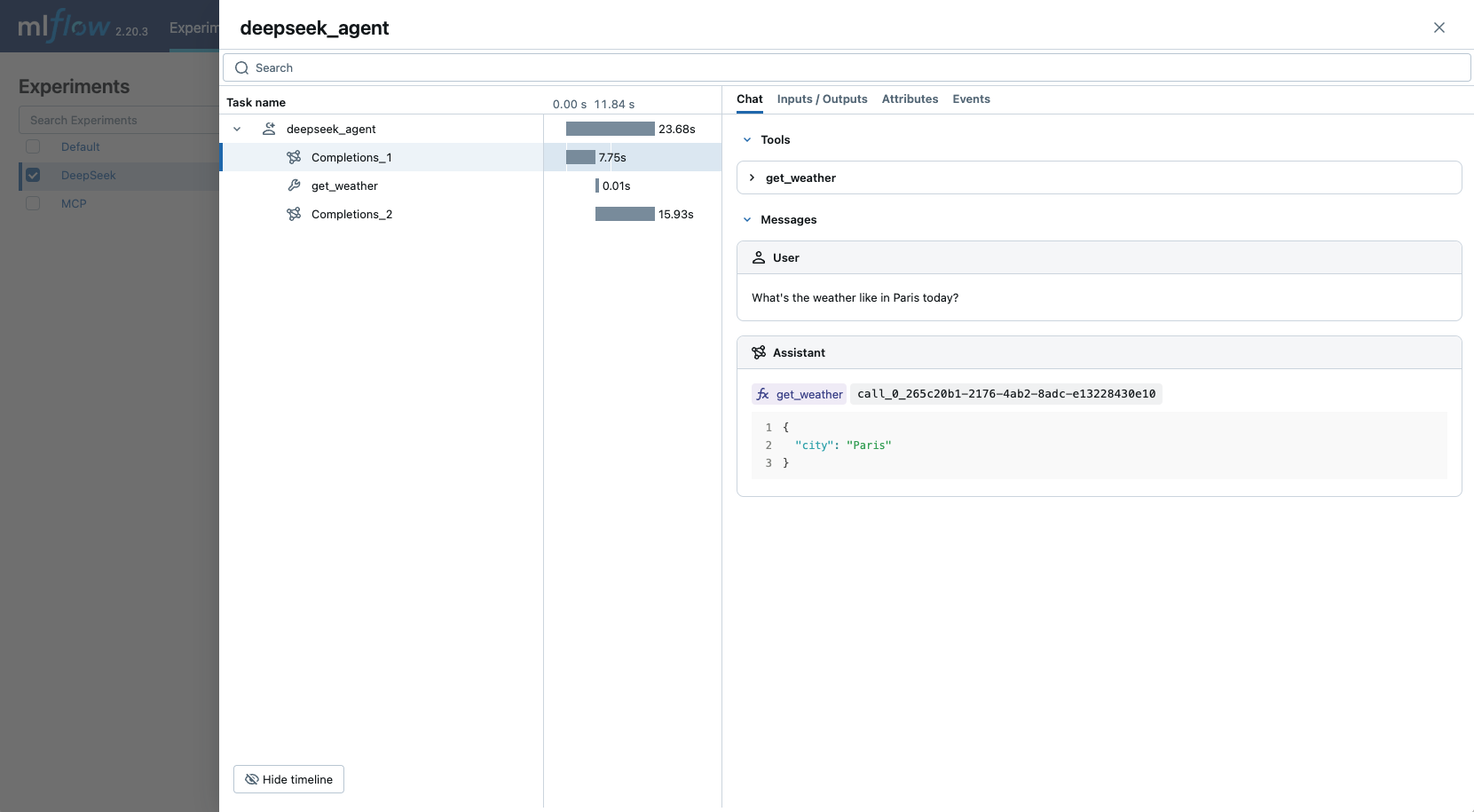
The above example should generate a trace in the DeepSeek experiment in the MLflow UI:

Streaming and Async Support
MLflow supports tracing for streaming and async DeepSeek APIs. Visit the OpenAI Tracing documentation for example code snippets for tracing streaming and async calls through OpenAI SDK.
Advanced Example: Function Calling Agent
MLflow Tracing automatically captures function calling responses from DeepSeek models through the OpenAI SDK. The function instruction in the response will be highlighted in the trace UI. Moreover, you can annotate the tool function with the @mlflow.trace decorator to create a span for the tool execution.
The following example implements a simple function calling agent using DeepSeek Function Calling and MLflow Tracing.
import json
from openai import OpenAI
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
# Initialize the OpenAI client with DeepSeek API endpoint
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://api.deepseek.com", api_key="<your_deepseek_api_key>")
# Define the tool function. Decorate it with `@mlflow.trace` to create a span for its execution.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
if city == "Tokyo":
return "sunny"
elif city == "Paris":
return "rainy"
return "unknown"
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"city": {"type": "string"}},
},
},
}
]
_tool_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
# Define a simple tool calling agent
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
def run_tool_agent(question: str):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": question}]
# Invoke the model with the given question and available tools
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
)
ai_msg = response.choices[0].message
messages.append(ai_msg)
# If the model request tool call(s), invoke the function with the specified arguments
if tool_calls := ai_msg.tool_calls:
for tool_call in tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
if tool_func := _tool_functions.get(function_name):
args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
tool_result = tool_func(**args)
else:
raise RuntimeError("An invalid tool is returned from the assistant!")
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": tool_result,
}
)
# Sent the tool results to the model and get a new response
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat", messages=messages
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
# Run the tool calling agent
question = "What's the weather like in Paris today?"
answer = run_tool_agent(question)
Token usage
MLflow >= 3.2.0 supports token usage tracking for Deepseek models through the OpenAI SDK integration. The token usage for each LLM call will be logged in the mlflow.chat.tokenUsage attribute. The total token usage throughout the trace will be
available in the token_usage field of the trace info object.
import json
import mlflow
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Run the tool calling agent defined in the previous section
question = "What's the weather like in Paris today?"
answer = run_tool_agent(question)
# Get the trace object just created
last_trace_id = mlflow.get_last_active_trace_id()
trace = mlflow.get_trace(trace_id=last_trace_id)
# Print the token usage
total_usage = trace.info.token_usage
print("== Total token usage: ==")
print(f" Input tokens: {total_usage['input_tokens']}")
print(f" Output tokens: {total_usage['output_tokens']}")
print(f" Total tokens: {total_usage['total_tokens']}")
# Print the token usage for each LLM call
print("\n== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==")
for span in trace.data.spans:
if usage := span.get_attribute("mlflow.chat.tokenUsage"):
print(f"{span.name}:")
print(f" Input tokens: {usage['input_tokens']}")
print(f" Output tokens: {usage['output_tokens']}")
print(f" Total tokens: {usage['total_tokens']}")
== Total token usage: ==
Input tokens: 84
Output tokens: 22
Total tokens: 106
== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==
Completions_1:
Input tokens: 45
Output tokens: 14
Total tokens: 59
Completions_2:
Input tokens: 39
Output tokens: 8
Total tokens: 47
Disable auto-tracing
Auto tracing for DeepSeek (through OpenAI SDK) can be disabled globally by calling mlflow.openai.autolog(disable=True) or mlflow.autolog(disable=True).