Tracing Anthropic
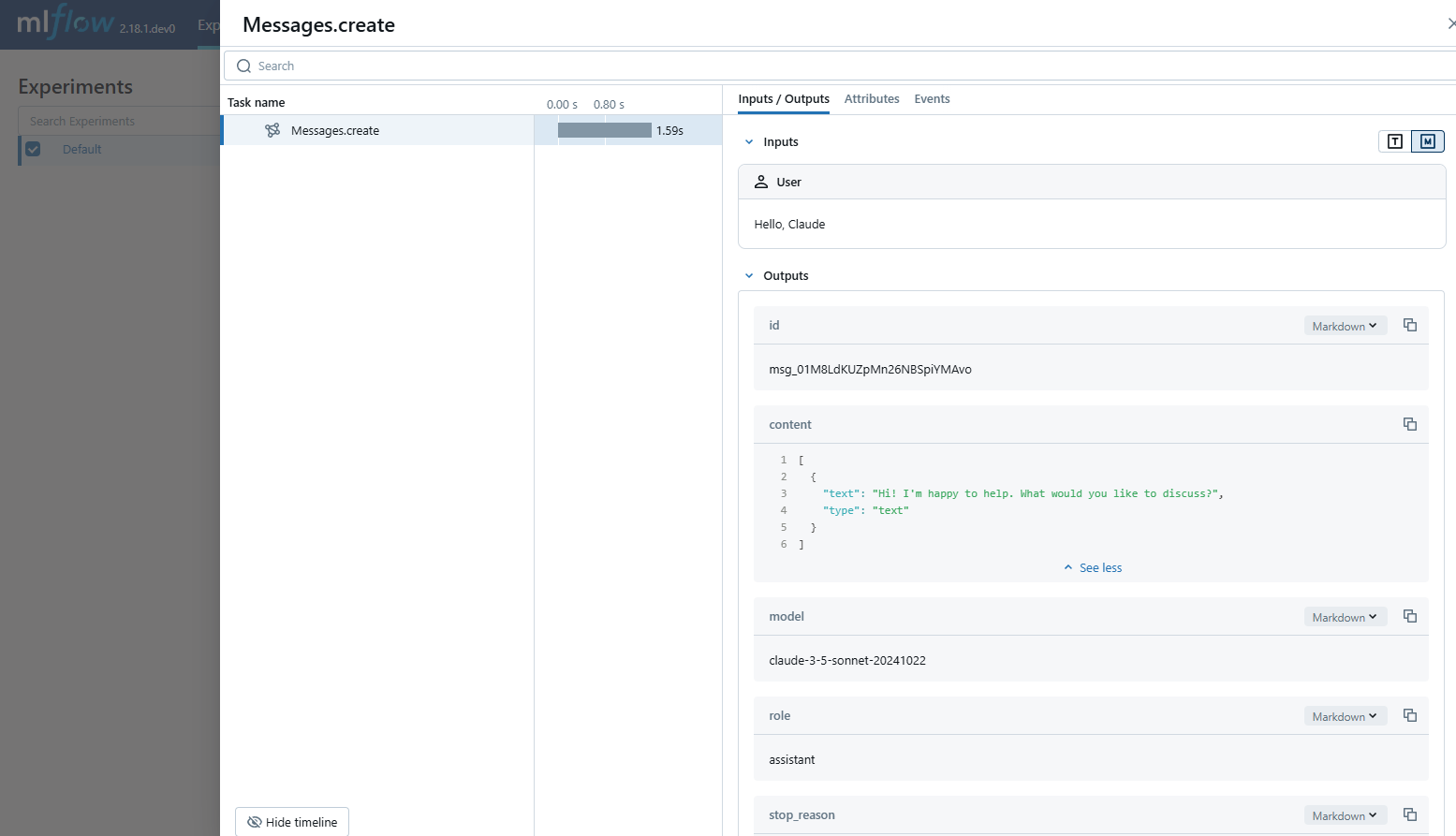
MLflow Tracing provides automatic tracing capability for Anthropic LLMs. By enabling auto tracing
for Anthropic by calling the mlflow.anthropic.autolog() function, MLflow will capture nested traces and log them to the active MLflow Experiment upon invocation of Anthropic Python SDK.
import mlflow
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
MLflow trace automatically captures the following information about Anthropic calls:
- Prompts and completion responses
- Latencies
- Model name
- Additional metadata such as
temperature,max_tokens, if specified. - Function calling if returned in the response
- Any exception if raised
Currently, MLflow Anthropic integration only support tracing for synchronous calls for text interactions. Async APIs are not traced, and full inputs cannot be recorded for multi-modal inputs.
Supported APIs
MLflow supports automatic tracing for the following Anthropic APIs:
| Chat Completion | Function Calling | Streaming | Async | Image | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | - | ✅ (*1) | - | - |
(*1) Async support was added in MLflow 2.21.0.
To request support for additional APIs, please open a feature request on GitHub.
Basic Example
import anthropic
import mlflow
# Enable auto-tracing for Anthropic
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
# Optional: Set a tracking URI and an experiment
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("http://localhost:5000")
mlflow.set_experiment("Anthropic")
# Configure your API key.
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key=os.environ["ANTHROPIC_API_KEY"])
# Use the create method to create new message.
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Async
MLflow Tracing has supported the asynchronous API of the Anthropic SDK since MLflow 2.21.0. Its usage is the same as the synchronous API.
import anthropic
# Enable trace logging
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Advanced Example: Tool Calling Agent
MLflow Tracing automatically captures tool calling response from Anthropic models. The function instruction in the response will be highlighted in the trace UI. Moreover, you can annotate the tool function with the @mlflow.trace decorator to create a span for the tool execution.
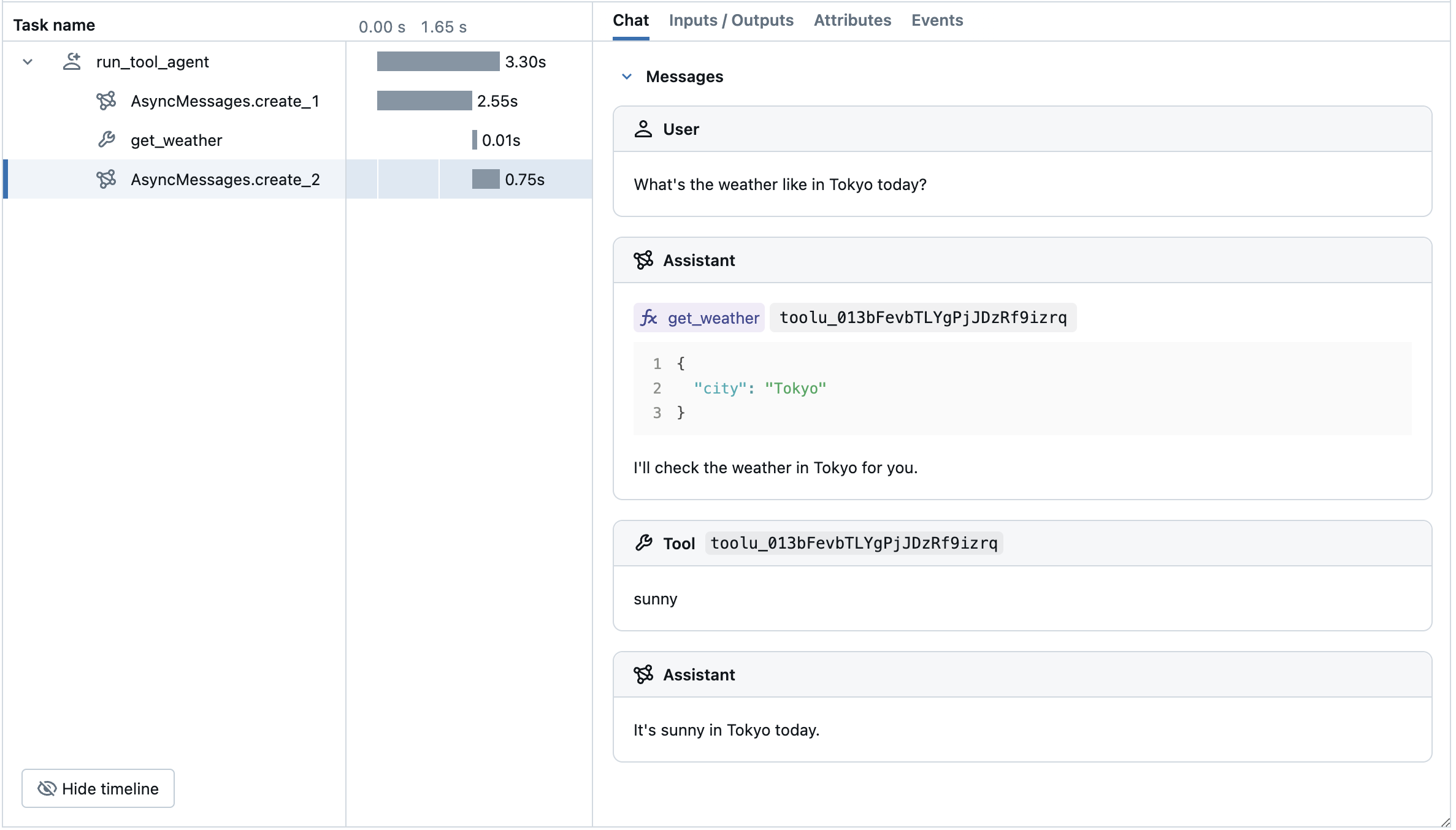
The following example implements a simple function calling agent using Anthropic Tool Calling and MLflow Tracing for Anthropic. The example further uses the asynchronous Anthropic SDK so that the agent can handle concurrent invocations without blocking.
import json
import anthropic
import mlflow
import asyncio
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
model_name = "claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022"
# Define the tool function. Decorate it with `@mlflow.trace` to create a span for its execution.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
async def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
if city == "Tokyo":
return "sunny"
elif city == "Paris":
return "rainy"
return "unknown"
tools = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Returns the weather condition of a given city.",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"city": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["city"],
},
}
]
_tool_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
# Define a simple tool calling agent
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
async def run_tool_agent(question: str):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": question}]
# Invoke the model with the given question and available tools
ai_msg = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
max_tokens=2048,
)
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": ai_msg.content})
# If the model requests tool call(s), invoke the function with the specified arguments
tool_calls = [c for c in ai_msg.content if c.type == "tool_use"]
for tool_call in tool_calls:
if tool_func := _tool_functions.get(tool_call.name):
tool_result = await tool_func(**tool_call.input)
else:
raise RuntimeError("An invalid tool is returned from the assistant!")
messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_call.id,
"content": tool_result,
}
],
}
)
# Send the tool results to the model and get a new response
response = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
max_tokens=2048,
)
return response.content[-1].text
# Run the tool calling agent
cities = ["Tokyo", "Paris", "Sydney"]
questions = [f"What's the weather like in {city} today?" for city in cities]
answers = await asyncio.gather(*(run_tool_agent(q) for q in questions))
for city, answer in zip(cities, answers):
print(f"{city}: {answer}")
Disable auto-tracing
Auto tracing for Anthropic can be disabled globally by calling mlflow.anthropic.autolog(disable=True) or mlflow.autolog(disable=True).